
Applications for the LAMP Fellowship 2026-27 are closed. Shortlisted candidates will be asked to take an online test on January 4, 2026.
As of May 11, 2020, there are 67,152 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in India. Since May 4, 24,619 new cases have been registered. Out of the confirmed cases so far, 20,917 patients have been cured/discharged and 2,206 have died. As the spread of COVID-19 has increased across the country, the central government has continued to announce several policy decisions to contain the spread, and support citizens and businesses who are being affected by the pandemic. In this blog post, we summarise some of the key measures taken by the central government in this regard between May 4 and May 11, 2020.
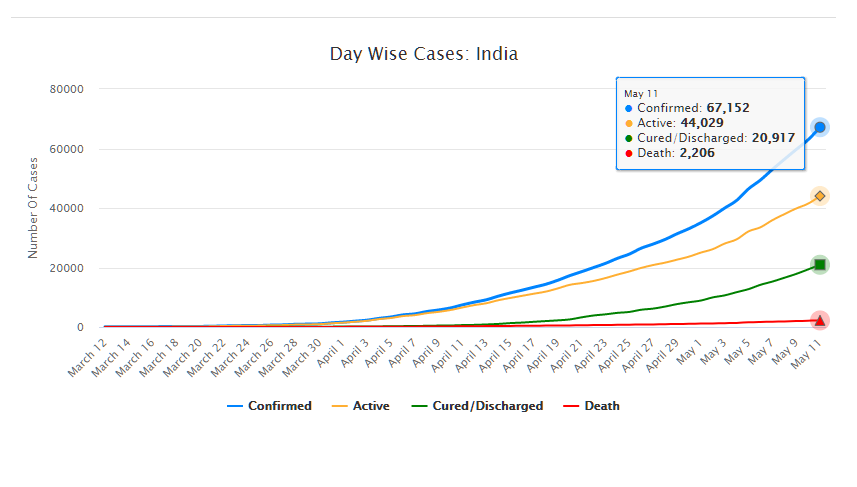
Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; PRS.
Industry
Relaxation of labour laws in some states
The Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Uttarakhand governments have passed notifications to increase maximum weekly work hours from 48 hours to 72 hours and daily work hours from 9 hours to 12 hours for certain factories. This was done to combat the shortage of labour caused by the lockdown. Further, some state governments stated that longer shifts would ensure a fewer number of workers in factories so as to allow for social distancing.
Madhya Pradesh has promulgated the Madhya Pradesh Labour Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020. The Ordinance exempts establishments with less than 100 workers from adhering to the Madhya Pradesh Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1961, which regulates the conditions of employment of workers. Further, it allows the state government to exempt any establishment or class of establishments from the Madhya Pradesh Shram Kalyan Nidhi Adhiniyam, 1982, which provides for the constitution of a welfare fund for labour.
The Uttar Pradesh government has published a draft Ordinance which exempts all factories and establishments engaged in manufacturing processes from all labour laws for a period of three years. Certain conditions will continue to apply with regard to payment of wages, safety, compensation and work hours, amongst others. However, labour laws providing for social security, industrial dispute resolution, trade unions, strikes, amongst others, will not apply under the Ordinance.
Financial aid
Central government signs an agreement with Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank for COVID-19 support
The central government and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a 500 million dollar agreement for the COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project. The project aims to help India respond to the COVID-19 pandemic and strengthen India’s public health system to manage future disease outbreaks. The project is being financed by the World Bank and AIIB in the amount of 1.5 billion dollars, of which one billion dollars is being provided by World Bank and 500 million dollars is being provided by AIIB. This financial support will be available to all states and union territories and will be used to address the needs of at-risk populations, medical personnel, and creating medical and testing facilities, amongst others. The project will be implemented by the National Health Mission, the National Center for Disease Control, and the Indian Council of Medical Research, under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Travel
Restarting of passenger travel by railways
Indian Railways plans to restart passenger trains from May 12 onwards. It will begin with 15 pairs of trains which will run from New Delhi station connecting Dibrugarh, Agartala, Howrah, Patna, Bilaspur, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar, Secunderabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Madgaon, Mumbai Central, Ahmedabad and Jammu Tawi. Booking for reservation in these trains will start at 4 pm on May 11. Thereafter, Indian Railways plans to start more services on new routes.
Return of Indians stranded abroad
The central government will facilitate the return of Indian nationals stranded abroad in a phased manner beginning on May 7. The travel will be arranged by aircraft and naval ships. The stranded Indians utilising the service will be required to pay for it. Medical screening of the passengers will be done before the flight. On reaching India, passengers will be required to download the Aarogya Setu app. Further, they will be quarantined by the concerned state government in either a hospital or a quarantine institution for 14 days on a payment basis. After quarantine, passengers will be tested for COVID-19 and further action will be taken based on the results.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.
In light of the decision of the union cabinet to promulgate an Ordinance to uphold provisions of the Representation of People Act, 1951, this blog examines the Ordinance making power of the Executive in India. The Ordinance allows legislators (Members of Parliament and Members of Legislative Assemblies) to retain membership of the legislature even after conviction, if (a) an appeal against the conviction is filed before a court within 90 days and (b) the appeal is stayed by the court. However, the Ordinance will only be promulgated after it receives the assent of the President. I. Separation of powers between the Legislature, Executive and Judiciary In India, the central and state legislatures are responsible for law making, the central and state governments are responsible for the implementation of laws and the judiciary (Supreme Court, High Courts and lower courts) interprets these laws. However, there are several overlaps in the functions and powers of the three institutions. For example, the President has certain legislative and judicial functions and the legislature can delegate some of its functions to the executive in the form of subordinate legislation. II. Ordinance making powers of the President Article 123 of the Constitution grants the President certain law making powers to promulgate Ordinances when either of the two Houses of Parliament is not in session and hence it is not possible to enact laws in the Parliament.[i] An Ordinance may relate to any subject that the Parliament has the power to legislate on. Conversely, it has the same limitations as the Parliament to legislate, given the distribution of powers between the Union, State and Concurrent Lists. Thus, the following limitations exist with regard to the Ordinance making power of the executive: i. Legislature is not in session: The President can only promulgate an Ordinance when either of the two Houses of Parliament is not in session. ii. Immediate action is required: The President cannot promulgate an Ordinance unless he is satisfied that there are circumstances that require taking ‘immediate action’[ii]. iii. Parliamentary approval during session: Ordinances must be approved by Parliament within six weeks of reassembling or they shall cease to operate. They will also cease to operate in case resolutions disapproving the Ordinance are passed by both the Houses. Figure 1 shows the number of Ordinances that have been promulgated in India since 1990. The largest number of Ordinances was promulgated in 1993, and there has been a decline in the number of Ordinance promulgated since then. However, the past year has seen a rise in the number of Ordinances promulgated. Figure 1: Number of national Ordinances promulgated in India since 1990  Source: Ministry of Law and Justice; Agnihotri, VK (2009) ‘The Ordinance: Legislation by the Executive in India when the Parliament is not in Session’; PRS Legislative Research III. Ordinance making powers of the Governor Just as the President of India is constitutionally mandated to issue Ordinances under Article 123, the Governor of a state can issue Ordinances under Article 213, when the state legislative assembly (or either of the two Houses in states with bicameral legislatures) is not in session. The powers of the President and the Governor are broadly comparable with respect to Ordinance making. However, the Governor cannot issue an Ordinance without instructions from the President in three cases where the assent of the President would have been required to pass a similar Bill.[iii] IV. Key debates relating to the Ordinance making powers of the Executive There has been significant debate surrounding the Ordinance making power of the President (and Governor). Constitutionally, important issues that have been raised include judicial review of the Ordinance making powers of the executive; the necessity for ‘immediate action’ while promulgating an Ordinance; and the granting of Ordinance making powers to the executive, given the principle of separation of powers. Table 1 provides a brief historical overview of the manner in which the debate on the Ordinance making powers of the executive has evolved in India post independence. Table 1: Key debates on the President's Ordinance making power
Source: Ministry of Law and Justice; Agnihotri, VK (2009) ‘The Ordinance: Legislation by the Executive in India when the Parliament is not in Session’; PRS Legislative Research III. Ordinance making powers of the Governor Just as the President of India is constitutionally mandated to issue Ordinances under Article 123, the Governor of a state can issue Ordinances under Article 213, when the state legislative assembly (or either of the two Houses in states with bicameral legislatures) is not in session. The powers of the President and the Governor are broadly comparable with respect to Ordinance making. However, the Governor cannot issue an Ordinance without instructions from the President in three cases where the assent of the President would have been required to pass a similar Bill.[iii] IV. Key debates relating to the Ordinance making powers of the Executive There has been significant debate surrounding the Ordinance making power of the President (and Governor). Constitutionally, important issues that have been raised include judicial review of the Ordinance making powers of the executive; the necessity for ‘immediate action’ while promulgating an Ordinance; and the granting of Ordinance making powers to the executive, given the principle of separation of powers. Table 1 provides a brief historical overview of the manner in which the debate on the Ordinance making powers of the executive has evolved in India post independence. Table 1: Key debates on the President's Ordinance making power
| Year |
Legislative development |
Key arguments |
| 1970 | RC Cooper vs. Union of India | In RC Cooper vs. Union of India (1970) the Supreme Court, while examining the constitutionality of the Banking Companies (Acquisition of Undertakings) Ordinance, 1969 which sought to nationalise 14 of India’s largest commercial banks, held that the President’s decision could be challenged on the grounds that ‘immediate action’ was not required; and the Ordinance had been passed primarily to by-pass debate and discussion in the legislature. |
| 1975 | 38th Constitutional Amendment Act | Inserted a new clause (4) in Article 123 stating that the President’s satisfaction while promulgating an Ordinance was final and could not be questioned in any court on any ground. |
| 1978 | 44th Constitutional Amendment Act | Deleted clause (4) inserted by the 38th CAA and therefore reopened the possibility for the judicial review of the President’s decision to promulgate an Ordinance. |
| 1980 | AK Roy vs. Union of India | In AK Roy vs. Union of India (1982) while examining the constitutionality of the National Security Ordinance, 1980, which sought to provide for preventive detention in certain cases, the Court argued that the President’s Ordinance making power is not beyond the scope of judicial review. However, it did not explore the issue further as there was insufficient evidence before it and the Ordinance was replaced by an Act. It also pointed out the need to exercise judicial review over the President’s decision only when there were substantial grounds to challenge the decision, and not at “every casual and passing challenge”. |
| 1985 | T Venkata Reddy vs. State of Andhra Pradesh | In T Venkata Reddy vs. State of Andhra Pradesh (1985), while deliberating on the promulgation of the Andhra Pradesh Abolition of Posts of Part-time Village Officers Ordinance, 1984 which abolished certain village level posts, the Court reiterated that the Ordinance making power of the President and the Governor was a legislative power, comparable to the legislative power of the Parliament and state legislatures respectively. This implies that the motives behind the exercise of this power cannot be questioned, just as is the case with legislation by the Parliament and state legislatures. |
| 1987 | DC Wadhwa vs. State of Bihar | It was argued in DC Wadhwa vs. State of Bihar (1987) the legislative power of the executive to promulgate Ordinances is to be used in exceptional circumstances and not as a substitute for the law making power of the legislature. Here, the court was examining a case where a state government (under the authority of the Governor) continued to re-promulgate ordinances, that is, it repeatedly issued new Ordinances to replace the old ones, instead of laying them before the state legislature. A total of 259 Ordinances were re-promulgated, some of them for as long as 14 years. The Supreme Court argued that if Ordinance making was made a usual practice, creating an ‘Ordinance raj’ the courts could strike down re-promulgated Ordinances. |
Source: Basu, DD (2010) Introduction to the Constitution of India; Singh, Mahendra P. (2008) VN Shukla's Constitution of India; PRS Legislative Research
This year, the following 9 Ordinances have been promulgated:
Three of these Ordinances have been re-promulgated, i.e., a second Ordinance has been promulgated to replace an existing one. This seems to be in violation of the Supreme Court’s decision in DC Wadhwa vs. State of Bihar.
Notes: [i] With regard to issuing Ordinances as with other matters, the President acts on the advice of the Council of Ministers. While the Ordinance is promulgated in the name of the President and constitutionally to his satisfaction, in fact, it is promulgated on the advice of the Council of Ministers.
[ii] Article 123, Clause (1)
[iii] (a) if a Bill containing the same provisions would have required the previous sanction of the President for introduction into the legislature; (b) if the Governor would have deemed it necessary to reserve a Bill containing the same provisions for the consideration of the President; and (c) if an Act of the legislature containing the same provisions would have been invalid unless it received the assent of the President.