
Applications for the LAMP Fellowship 2026-27 are open now. Apply here
As of May 11, 2020, there are 67,152 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in India. Since May 4, 24,619 new cases have been registered. Out of the confirmed cases so far, 20,917 patients have been cured/discharged and 2,206 have died. As the spread of COVID-19 has increased across the country, the central government has continued to announce several policy decisions to contain the spread, and support citizens and businesses who are being affected by the pandemic. In this blog post, we summarise some of the key measures taken by the central government in this regard between May 4 and May 11, 2020.
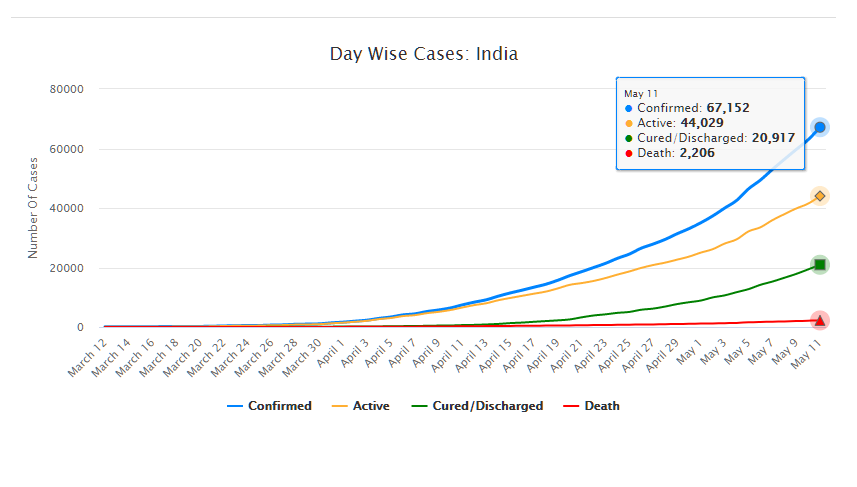
Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; PRS.
Industry
Relaxation of labour laws in some states
The Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Uttarakhand governments have passed notifications to increase maximum weekly work hours from 48 hours to 72 hours and daily work hours from 9 hours to 12 hours for certain factories. This was done to combat the shortage of labour caused by the lockdown. Further, some state governments stated that longer shifts would ensure a fewer number of workers in factories so as to allow for social distancing.
Madhya Pradesh has promulgated the Madhya Pradesh Labour Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020. The Ordinance exempts establishments with less than 100 workers from adhering to the Madhya Pradesh Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1961, which regulates the conditions of employment of workers. Further, it allows the state government to exempt any establishment or class of establishments from the Madhya Pradesh Shram Kalyan Nidhi Adhiniyam, 1982, which provides for the constitution of a welfare fund for labour.
The Uttar Pradesh government has published a draft Ordinance which exempts all factories and establishments engaged in manufacturing processes from all labour laws for a period of three years. Certain conditions will continue to apply with regard to payment of wages, safety, compensation and work hours, amongst others. However, labour laws providing for social security, industrial dispute resolution, trade unions, strikes, amongst others, will not apply under the Ordinance.
Financial aid
Central government signs an agreement with Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank for COVID-19 support
The central government and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a 500 million dollar agreement for the COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project. The project aims to help India respond to the COVID-19 pandemic and strengthen India’s public health system to manage future disease outbreaks. The project is being financed by the World Bank and AIIB in the amount of 1.5 billion dollars, of which one billion dollars is being provided by World Bank and 500 million dollars is being provided by AIIB. This financial support will be available to all states and union territories and will be used to address the needs of at-risk populations, medical personnel, and creating medical and testing facilities, amongst others. The project will be implemented by the National Health Mission, the National Center for Disease Control, and the Indian Council of Medical Research, under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Travel
Restarting of passenger travel by railways
Indian Railways plans to restart passenger trains from May 12 onwards. It will begin with 15 pairs of trains which will run from New Delhi station connecting Dibrugarh, Agartala, Howrah, Patna, Bilaspur, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar, Secunderabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Madgaon, Mumbai Central, Ahmedabad and Jammu Tawi. Booking for reservation in these trains will start at 4 pm on May 11. Thereafter, Indian Railways plans to start more services on new routes.
Return of Indians stranded abroad
The central government will facilitate the return of Indian nationals stranded abroad in a phased manner beginning on May 7. The travel will be arranged by aircraft and naval ships. The stranded Indians utilising the service will be required to pay for it. Medical screening of the passengers will be done before the flight. On reaching India, passengers will be required to download the Aarogya Setu app. Further, they will be quarantined by the concerned state government in either a hospital or a quarantine institution for 14 days on a payment basis. After quarantine, passengers will be tested for COVID-19 and further action will be taken based on the results.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.
As of May 4, 2020, there are 42,533 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in India. Since April 27, 14,641 new cases have been registered. Out of the confirmed cases so far, 11,707 patients have been cured/discharged and 1,373 have died. As the spread of COVID-19 has increased across India, the central government has continued to announce several policy decisions to contain the spread, and support citizens and businesses who are being affected by the pandemic. In this blog post, we summarise some of the key measures taken by the central government in this regard between April 27 and May 4, 2020.
Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; PRS.
Lockdown
Extension of lockdown until May 18, 2020
The Ministry of Home Affairs passed an order extending the lockdown for two weeks from May 4, 2020 (until May 18, 2020). Activities that remain prohibited in the extended lockdown include:
Travel and movement: Passenger movement by: (i) air (except for medical and security purposes), (ii) trains (except for security purposes), (iii) inter-state buses (unless permitted by central government), and (iv) metro, remains prohibited. Inter-state movement of individuals is also prohibited except for medical reasons or if permitted by the central government. Intra-state movement of persons for all non-essential activities will remain prohibited between 7pm and 7am.
Education: All educational institutions such as schools and colleges will remain closed except for online learning.
Hospitality services and recreational activities: All hospitality services such as hotels will remain closed except those being used as quarantine facilities, or those housing persons such as healthcare workers, police, or stranded persons. Further, recreational facilities such as cinemas, malls, gyms, and bars will remain closed.
Religious gatherings: All religious spaces will remain closed and congregation for religious purposes will remain prohibited.
The revised guidelines for the lockdown include risk-profiling of districts into red, green and orange zones. Zone classifications will be decided by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and shared with states on a weekly basis. States may include additional districts as red or orange zones. However, they may not lower the classification of any district. For a district to move from a red zone to an orange zone, or from an orange zone to a green zone, it must have no new cases for 21 days. Classification of and activities permitted in the zones include:
Red zones or hotspots: These districts will be identified based on the total number of active cases, doubling rate of confirmed cases, and testing and surveillance feedback. Additional activities prohibited in red zones include: (i) cycle and auto rickshaws, (ii) taxis, (iii) buses, and (iv) barber shops, spas and salons. Activities that are permitted include: (i) movement of individuals (maximum two persons in four wheelers, and one person in two wheelers), (ii) all industrial establishments in rural areas and certain industrial establishments in urban areas such as manufacturing of essential goods, and (iii) all standalone and neighbourhood shops.
Green zones: These zones include districts with no confirmed cases till date or no confirmed cases in the last 21 days. No additional activities are prohibited in these zones. In addition to activities permitted in red zones, buses can operate with up to 50% seating capacity.
Orange zones: These zones include all districts that do not fall in either red or green zones. Inter and intra-state plying of buses is prohibited in these zones. Activities that are permitted (in addition to those permitted in red zones) include: (i) taxis with a maximum of one driver and two passengers, (ii) inter-district movement of individuals and vehicles for permitted activities, and (iii) four wheeler vehicles with a maximum of one driver and two passengers.
Certain areas within red and orange zones will be identified as containment zones by the district administration. Containment zones may include areas such as residential colonies, towns, or municipal wards. In containment zones, local authorities must ensure 100% coverage of Aarogya Setu App, contract tracing, quarantine of individuals based on risk, and house to house surveillance. Further, movement of persons in or out will be prohibited except for medical emergencies and essential goods, amongst other measures.
Movement of stranded persons
The Ministry of Home Affairs has permitted the movement of migrant workers, pilgrims, tourists, students, and other stranded persons, by special trains. To facilitate this, all states and union territories will designate nodal authorities for sending, receiving, and registering stranded persons. The state sending persons and the state receiving persons both need to agree to the exchange. Each train can carry up to 1,200 persons and no train may run at less than 90% capacity. Passengers approved for travel by the state governments may be required to pay some part of the ticket fare.
Education
UGC issues guidelines on examinations and the academic calendar for universities
The University Grants Commission (UGC) issued guidelines on examinations and the academic calendar for universities in view of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Academic Calendar: Classes for the even semester in universities were suspended from March 16, 2020 onwards. The guidelines prescribe that online teaching must continue till May 31 through social media (WhatsApp / YouTube), emails, or video conferencing. The examinations for the current academic year should be held in July, 2020 and the results for the same should be declared by July 31 (for terminal year students) and by August 14 (for intermediate year students)
The Academic Session 2020-21 may commence from August 2020 for old students and from September 2020 for fresh students. The admission process for the fresh students can be done in August. Consequently, the commencement of even semester for 2020-21 can be from January 27, 2021. The commencement of academic session 2021-22 may be from August 2021. The universities may follow a 6-day week pattern to compensate the loss of teaching for the remaining session of 2019- 20 and the 2020-21 academic session.
Examination: The universities may conduct semester or yearly examinations in offline or online mode. This has to be done while observing the guidelines of “social distancing” and ensuring fair opportunity for all students. They may adopt alternative, simplified methods of examinations such as multiple choice questions based examinations or open book examination. If examinations cannot be conducted in view of the prevailing situation at the time, grading may be done on the basis of internal assessments and performance in previous semester. The universities may conduct the Ph.D viva examinations through video conferencing.
Other guidelines: Every University should establish a COVID-19 cell for handling student grievances related to examinations and academic activities during the pandemic and notify effectively to the students. Further, a COVID-19 cell will be created in the UGC for faster decision making.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.