
In April 2020, the International Labour Organisation (ILO) estimated that nearly 2.5 crore jobs could be lost worldwide due to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. Further, it observed that more than 40 crore informal workers in India may get pushed into deeper poverty due to the pandemic. In this blog post, we discuss the effect of COVID-19 on unemployment in urban areas as per the quarterly Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) report released last week, and highlight some of the measures taken by the central government with regard to unemployment.
|
Methodology for estimating unemployment in PLFS reports The National Statistics Office (NSO) released its latest quarterly PLFS report for the October-December 2020 quarter. The PLFS reports give estimates of labour force indicators including Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR), Unemployment Rate, and distribution of workers across industries. The reports are released on a quarterly as well as annual basis. The quarterly reports cover only urban areas whereas the annual report covers both urban and rural areas. The latest annual report is available for the July 2019-June 2020 period. The quarterly PLFS reports provide estimates based on the Current Weekly Activity Status (CWS). The CWS of a person is the activity status obtained during a reference period of seven days preceding the date of the survey. As per CWS status, a person is considered as unemployed in a week if he did not work even for at least one hour on any day during the reference week but sought or was available for work. In contrast, the headline numbers on employment-unemployment in the annual PLFS reports are reported based on the usual activity status. Usual activity status relates to the activity status of a person during the reference period of the last 365 days preceding the date of the survey. |
To contain the spread of COVID-19, a nationwide lockdown was imposed from late March till May 2020. During the lockdown, severe restrictions were placed on the movement of individuals and economic activities were significantly halted barring the activities related to essential goods and services. Unemployment rate in urban areas rose to 20.9% during the April-June quarter of 2020, more than double the unemployment rate in the same quarter the previous year (8.9%). Unemployment rate refers to the percentage of unemployed persons in the labour force. Labour force includes persons who are either employed or unemployed but seeking work. The lockdown restrictions were gradually relaxed during the subsequent months. Unemployment rate also saw a decrease as compared to the levels seen in the April-June quarter of 2020. During the October-December quarter of 2020 (latest data available), unemployment rate had reduced to 10.3%. However, it was notably higher than the unemployment rate in the same quarter last year (7.9%).
Figure 1: Unemployment rate in urban areas across all age groups as per current weekly activity status (Figures in %)
Note: PLFS includes data for transgenders among males.
Sources: Quarterly Periodic Labour Force Survey Reports, Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation; PRS.
Recovery post-national lockdown uneven in case of females
Pre-COVID-19 trends suggest that the female unemployment rate has generally been higher than the male unemployment rate in the country (7.3% vs 9.8% during the October-December quarter of 2019, respectively). Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, this gap seems to have widened. During the October-December quarter of 2020, the unemployment rate for females was 13.1%, as compared to 9.5% for males.
The Standing Committee on Labour (April 2021) also noted that the pandemic led to large-scale unemployment for female workers, in both organised and unorganised sectors. It recommended: (i) increasing government procurement from women-led enterprises, (ii) training women in new technologies, (iii) providing women with access to capital, and (iv) investing in childcare and linked infrastructure.
Labour force participation
Persons dropping in and out of the labour force may also influence the unemployment rate. At a given point of time, there may be persons who are below the legal working age or may drop out of the labour force due to various socio-economic reasons, for instance, to pursue education. At the same time, there may also be discouraged workers who, while willing and able to be employed, have ceased to seek work. Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) is the indicator that denotes the percentage of the population which is part of the labour force. The LFPR saw only marginal changes throughout 2019 and 2020. During the April-June quarter (where COVID-19 restrictions were the most stringent), the LFPR was 35.9%, which was lower than same in the corresponding quarter in 2019 (36.2%). Note that female LFPR in India is significantly lower than male LFPR (16.6% and 56.7%, respectively, in the October-December quarter of 2019).
Figure 2: LFPR in urban areas across all groups as per current weekly activity status (Figures in %)
Note: PLFS includes data for transgenders among males.
Sources: Quarterly Periodic Labour Force Survey Reports, Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation; PRS.
Measures taken by the government for workers
The Standing Committee on Labour in its report released in August 2021 noted that 90% of workers in India are from the informal sector. These workers include: (i) migrant workers, (ii) contract labourers, (iii) construction workers, and (iv) street vendors. The Committee observed that these workers were worst impacted by the pandemic due to seasonality of employment and lack of employer-employee relationship in unorganised sectors. The Committee recommended central and state governments to: (i) encourage entrepreneurial opportunities, (ii) attract investment in traditional manufacturing sectors and developing industrial clusters, (iii) strengthen social security measures, (iv) maintain a database of workers in the informal sector, and (v) promote vocational training. It took note of the various steps taken by the central government to support workers and address the challenges and threats posed by the COVID-19 pandemic (applicable to urban areas):
The central and state governments have also taken various other measures, such as increasing spending on infrastructure creation and enabling access to cheaper lending for businesses, to sustain economic activity and boost employment generation.
As of May 11, 2020, there are 67,152 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in India. Since May 4, 24,619 new cases have been registered. Out of the confirmed cases so far, 20,917 patients have been cured/discharged and 2,206 have died. As the spread of COVID-19 has increased across the country, the central government has continued to announce several policy decisions to contain the spread, and support citizens and businesses who are being affected by the pandemic. In this blog post, we summarise some of the key measures taken by the central government in this regard between May 4 and May 11, 2020.
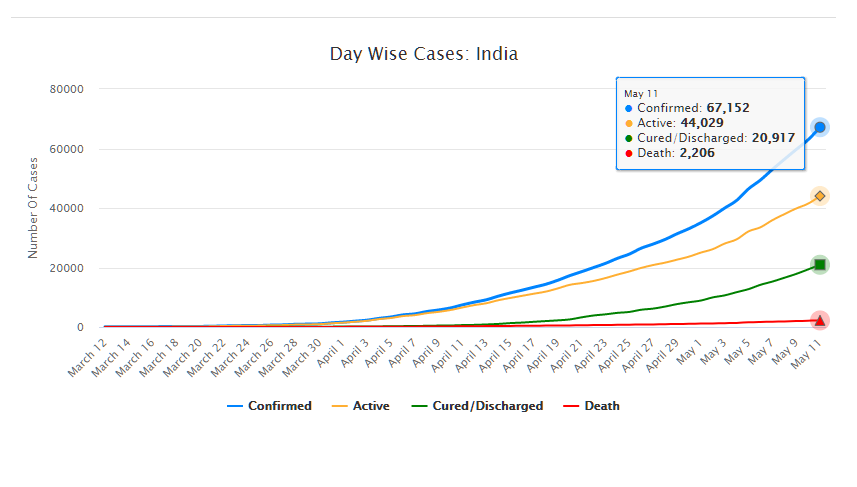
Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; PRS.
Industry
Relaxation of labour laws in some states
The Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Uttarakhand governments have passed notifications to increase maximum weekly work hours from 48 hours to 72 hours and daily work hours from 9 hours to 12 hours for certain factories. This was done to combat the shortage of labour caused by the lockdown. Further, some state governments stated that longer shifts would ensure a fewer number of workers in factories so as to allow for social distancing.
Madhya Pradesh has promulgated the Madhya Pradesh Labour Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020. The Ordinance exempts establishments with less than 100 workers from adhering to the Madhya Pradesh Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1961, which regulates the conditions of employment of workers. Further, it allows the state government to exempt any establishment or class of establishments from the Madhya Pradesh Shram Kalyan Nidhi Adhiniyam, 1982, which provides for the constitution of a welfare fund for labour.
The Uttar Pradesh government has published a draft Ordinance which exempts all factories and establishments engaged in manufacturing processes from all labour laws for a period of three years. Certain conditions will continue to apply with regard to payment of wages, safety, compensation and work hours, amongst others. However, labour laws providing for social security, industrial dispute resolution, trade unions, strikes, amongst others, will not apply under the Ordinance.
Financial aid
Central government signs an agreement with Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank for COVID-19 support
The central government and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a 500 million dollar agreement for the COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project. The project aims to help India respond to the COVID-19 pandemic and strengthen India’s public health system to manage future disease outbreaks. The project is being financed by the World Bank and AIIB in the amount of 1.5 billion dollars, of which one billion dollars is being provided by World Bank and 500 million dollars is being provided by AIIB. This financial support will be available to all states and union territories and will be used to address the needs of at-risk populations, medical personnel, and creating medical and testing facilities, amongst others. The project will be implemented by the National Health Mission, the National Center for Disease Control, and the Indian Council of Medical Research, under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Travel
Restarting of passenger travel by railways
Indian Railways plans to restart passenger trains from May 12 onwards. It will begin with 15 pairs of trains which will run from New Delhi station connecting Dibrugarh, Agartala, Howrah, Patna, Bilaspur, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar, Secunderabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Madgaon, Mumbai Central, Ahmedabad and Jammu Tawi. Booking for reservation in these trains will start at 4 pm on May 11. Thereafter, Indian Railways plans to start more services on new routes.
Return of Indians stranded abroad
The central government will facilitate the return of Indian nationals stranded abroad in a phased manner beginning on May 7. The travel will be arranged by aircraft and naval ships. The stranded Indians utilising the service will be required to pay for it. Medical screening of the passengers will be done before the flight. On reaching India, passengers will be required to download the Aarogya Setu app. Further, they will be quarantined by the concerned state government in either a hospital or a quarantine institution for 14 days on a payment basis. After quarantine, passengers will be tested for COVID-19 and further action will be taken based on the results.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.