
Our Constitution provides protection against laws imposing criminal liability for actions committed prior to the enactment of the law. Article 20 (1) under the Part III (Fundamental Rights), reads: 20. (1) No person shall be convicted of any offence except for violation of a law in force at the time of the commission of the act charged as an offence, nor be subjected to a penalty greater than that which might have been inflicted under the law in force at the time of the commission of the offence. Thus, the maximum penalty that can be imposed on an offender cannot exceed those specified by the laws at the time. In the context of the Bhopal Gas tragedy in 1984, the Indian Penal Code (IPC) was the only relevant law specifying criminal liability for such incidents. The CBI, acting on behalf of the victims, filed charges against the accused under section 304 of the IPC (See Note 1). Section 304 deals with punishment for culpable homicide and requires intention of causing death. By a judgment dated September 13, 1996, the Supreme Court held that there was no material to show that “any of the accused had a knowledge that by operating the plant on that fateful night whereat such dangerous and highly volatile substance like MIC was stored they had the knowledge that by this very act itself they were likely to cause death of any human being.” The Supreme Court thus directed that the charges be re-framed under section 304A of the IPC (See Note 2). Section 304A deals with causing death by negligence and prescribes a maximum punishment of two years along with a fine. Consequently, the criminal liability of the accused lay outlined by section 304A of the IPC and they were tried accordingly. Civil liability, on the other hand, was adjudged by the Courts and allocated to the victims by way of monetary compensation. Soon after the Bhopal Gas tragedy, the Government proposed and passed a series of laws regulating the environment, prescribing safeguards and specifying penalties. These laws, among other things, filled the legislative lacunae that existed at the time of the incident. Given the current provisions (See Note 3), a Bhopal like incident will be tried in the National Green Tribunal (once operationalized) and most likely, under the provisions of the the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. The criminal liability provisions of the Act (See Note 4) prescribe a maximum penalty of five years along with a fine of one lakh rupees. Further, if an offence is committed by a company, every person directly in charge and responsible will be deemed guilty, unless he proves that the offence was committed without his knowledge or that he had exercised all due diligence to prevent the commission of such an offence.
The civil liability will continue to be adjudged by the Courts and in proportion to the extent of damage unless specified separately by an Act of Parliament.
Notes 1) IPC, Section 304. Punishment for culpable homicide not amounting to murder Whoever commits culpable homicide not amounting to murder shall be punished with imprisonment for life, or imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to ten years, and shall also be liable to fine, if the act by which the death is caused is done with the intention of causing death, or of causing such bodily injury as is likely to cause death, Or with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to ten years, or with fine, or with both, if the act is done with the knowledge that it is likely to cause death, but without any intention to cause death, or to cause such bodily injury as is likely to cause death. 2) IPC, Section 304A. Causing death by negligence Whoever causes the death of any person by doing any rash or negligent act not amounting to culpable homicide, shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to two years, or with fine, or with both. 3) Major laws passed since 1984: 1986 - The Environment (Protection) Act authorized the central government to take measures to protect and improve environmental quality, set standards and inspect industrial units. It also laid down penalties for contravention of its provisions. 1991 - The Public Liability Insurance Act provided for public liability - insurance for the purpose of providing immediate relief to the persons affected by an accident while handling hazardous substances. 1997 - The National Environment Appellate Authority Act established to an appellate authority to hear appeals with respect to restriction of areas in which any industries, operations or processes are disallowed, subject to safeguards under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. 2009 - The National Green Tribunal Act, yet to be notified, provides for the establishment of a tribunal for expeditious disposal of cases relating to environmental protection and for giving relief and compensation for damages to persons and property. This Act also repeals the National Environment Appellate Authority Act, 1997. 4) Criminal liability provisions of the Environment Protection Act, 1986 Section 15. Penalty for contravention of the provisions of the Act (1) Whoever fails to comply with or contravenes any of the provisions of this Act, or the rules made or orders or directions issued thereunder, shall, in respect of each such failure or contravention, be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to five years with fine which may extend to one lakh rupees, or with both, and in case the failure or contravention continues, with additional fine which may extend to five thousand rupees for every day during which such failure or contravention continues after the conviction for the first such failure or contravention. (2) If the failure or contravention referred to in sub-section (1) continues beyond a period of one year after the date of conviction, the offender shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to seven years. Section 16. Offences by Companies (1) Where any offence under this Act has been committed by a company, every person who, at the time the offence was committed, was directly in charge of, and was responsible to, the company for the conduct of the business of the company, as well as the company, shall be deemed to be guilty of the offence and shall be liable to be proceeded against and punished accordingly: Provided that nothing contained in this sub-section shall render any such person liable to any punishment provided in this Act, if he proves that the offence was committed without his knowledge or that he exercised all due diligence to prevent the commission of such offence.
As of May 11, 2020, there are 67,152 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in India. Since May 4, 24,619 new cases have been registered. Out of the confirmed cases so far, 20,917 patients have been cured/discharged and 2,206 have died. As the spread of COVID-19 has increased across the country, the central government has continued to announce several policy decisions to contain the spread, and support citizens and businesses who are being affected by the pandemic. In this blog post, we summarise some of the key measures taken by the central government in this regard between May 4 and May 11, 2020.
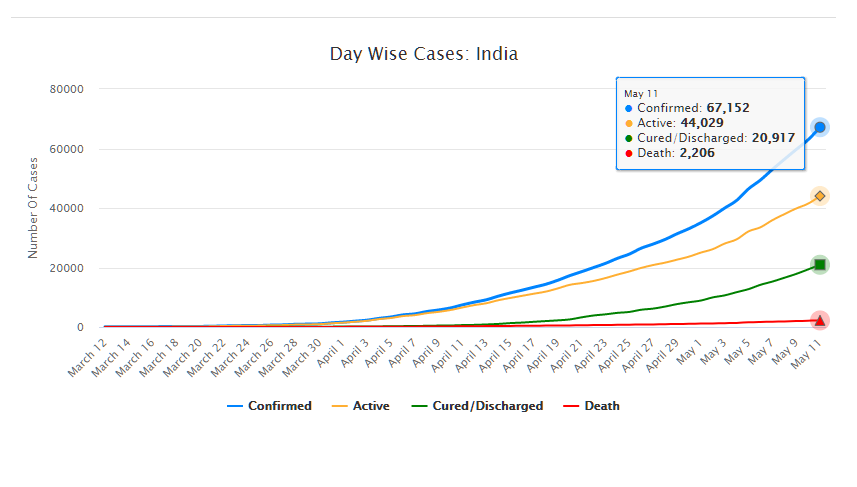
Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; PRS.
Industry
Relaxation of labour laws in some states
The Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Uttarakhand governments have passed notifications to increase maximum weekly work hours from 48 hours to 72 hours and daily work hours from 9 hours to 12 hours for certain factories. This was done to combat the shortage of labour caused by the lockdown. Further, some state governments stated that longer shifts would ensure a fewer number of workers in factories so as to allow for social distancing.
Madhya Pradesh has promulgated the Madhya Pradesh Labour Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020. The Ordinance exempts establishments with less than 100 workers from adhering to the Madhya Pradesh Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1961, which regulates the conditions of employment of workers. Further, it allows the state government to exempt any establishment or class of establishments from the Madhya Pradesh Shram Kalyan Nidhi Adhiniyam, 1982, which provides for the constitution of a welfare fund for labour.
The Uttar Pradesh government has published a draft Ordinance which exempts all factories and establishments engaged in manufacturing processes from all labour laws for a period of three years. Certain conditions will continue to apply with regard to payment of wages, safety, compensation and work hours, amongst others. However, labour laws providing for social security, industrial dispute resolution, trade unions, strikes, amongst others, will not apply under the Ordinance.
Financial aid
Central government signs an agreement with Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank for COVID-19 support
The central government and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a 500 million dollar agreement for the COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project. The project aims to help India respond to the COVID-19 pandemic and strengthen India’s public health system to manage future disease outbreaks. The project is being financed by the World Bank and AIIB in the amount of 1.5 billion dollars, of which one billion dollars is being provided by World Bank and 500 million dollars is being provided by AIIB. This financial support will be available to all states and union territories and will be used to address the needs of at-risk populations, medical personnel, and creating medical and testing facilities, amongst others. The project will be implemented by the National Health Mission, the National Center for Disease Control, and the Indian Council of Medical Research, under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Travel
Restarting of passenger travel by railways
Indian Railways plans to restart passenger trains from May 12 onwards. It will begin with 15 pairs of trains which will run from New Delhi station connecting Dibrugarh, Agartala, Howrah, Patna, Bilaspur, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar, Secunderabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Madgaon, Mumbai Central, Ahmedabad and Jammu Tawi. Booking for reservation in these trains will start at 4 pm on May 11. Thereafter, Indian Railways plans to start more services on new routes.
Return of Indians stranded abroad
The central government will facilitate the return of Indian nationals stranded abroad in a phased manner beginning on May 7. The travel will be arranged by aircraft and naval ships. The stranded Indians utilising the service will be required to pay for it. Medical screening of the passengers will be done before the flight. On reaching India, passengers will be required to download the Aarogya Setu app. Further, they will be quarantined by the concerned state government in either a hospital or a quarantine institution for 14 days on a payment basis. After quarantine, passengers will be tested for COVID-19 and further action will be taken based on the results.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.