
Applications for the LAMP Fellowship 2026-27 are closed. Shortlisted candidates will be asked to take an online test on January 4, 2026.
The Finance Bill, 2017 is being discussed in Lok Sabha today. Generally, the Finance Bill is passed as a Money Bill since it gives effect to tax changes proposed in the Union Budget. A Money Bill is defined in Article 110 of the Constitution as one which only contains provisions related to taxation, borrowings by the government, or expenditure from Consolidated Fund of India. A Money Bill only needs the approval of Lok Sabha, and is sent to Rajya Sabha for its recommendations. It is deemed to be passed by Rajya Sabha if it does not pass the Bill within 14 calendar days.
In addition to tax changes, the Finance Bill, 2017 proposes to amend several laws such the Securities Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 and the Payment and Settlements Act, 2007 to make structural changes such as creating a payments regulator and changing the composition of the Securities Appellate Tribunal. This week, some amendments to the Finance Bill were circulated. We discuss the provisions of the Bill, and the proposed amendments.
Certain Tribunals to be replaced
Amendments to the Finance Bill seek to replace certain Tribunals and transfer their functions to existing Tribunals. The rationale behind replacing these Tribunals is unclear. For example, the Telecom Disputes Settlement and Appellate Tribunal (TDSAT) will replace the Airports Economic Regulatory Authority Appellate Tribunal. It is unclear if TDSAT, which primarily deals with issues related to telecom disputes, will have the expertise to adjudicate matters related to the pricing of airport services. Similarly, it is unclear if the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal, which will replace the Competition Appellate Tribunal, will have the expertise to deal with matters related to anti-competitive practices.
Terms of service of Tribunal members to be determined by central government
The amendments propose that the central government may make rules to provide for the terms of service including appointments, term of office, salaries and allowances, and removal for Chairpersons and other members of Tribunals, Appellate Tribunals and other authorities. The amendments also cap the age of retirement for Chairpersons and Vice-Chairpersons. Currently, these terms are specified in the laws establishing these Tribunals.
One may argue that allowing the government to determine the appointment, reappointment and removal of members could affect the independent functioning of the Tribunals. There could be conflict of interest if the government were to be a litigant before a Tribunal as well as determine the appointment of its members and presiding officers.
The Supreme Court in 2014, while examining a case related to the National Tax Tribunal, had held that Appellate Tribunals have similar powers and functions as that of High Courts, and hence matters related to their members’ appointment and reappointment must be free from executive involvement.[i] The list of Tribunals under this amendment includes several Tribunals before which the central government could be a party to disputes, such as those related to income tax, railways, administrative matters, and the armed forces Tribunal.
Note that a Bill to establish uniform conditions of service for the chairpersons and members of some Tribunals has been pending in Parliament since 2014.
Inclusion of technical members in the Securities Appellate Tribunal
The composition of the Securities Appellate Tribunal established under the SEBI Act is being changed by the Finance Bill. Currently, the Tribunal consists of a Presiding Officer and two other members appointed by the central government. This composition is to be changed to: a Presiding Officer, and a number of judicial and technical members, as notified by the central government.
Creation of a Payments Regulatory Board
Recently, the Ratan Watal Committee under the Finance Ministry had recommended creating a statutory Payments Regulatory Board to oversee the payments systems in light of increase in digital payments. The Finance Bill, 2017 seeks to give effect to this recommendation by creating a Payments Regulatory Board chaired by the RBI Governor and including members nominated by the central government. This Board will replace the existing Board for Regulation and Supervision of Payment and Settlement Systems.
Political funding
The Finance Bill, 2017 proposes to make changes related to how donations may be made to political parties, and maintaining the anonymity of donors.
Currently, for donations below Rs 20,000, details of donors do not have to be disclosed by political parties. Further, there are no restrictions on the amount of cash donations that may be received by political parties from a person. The Finance Bill has proposed to set this limit at Rs 2,000. The Bill also introduces a new mode of donating to political parties, i.e. through electoral bonds. These bonds will be issued by banks, which may be bought through cheque or electronic means. The only difference between cheque payment (above Rs 20,000) and electoral bonds may be that the identity of the donor will be anonymous in the case of electoral bonds.
Regarding donations by companies to political parties, the proposed amendments to the Finance Bill remove the: (i) existing limit of contributions that a company may make to political parties which currently is 7.5% of net profit of the last three financial years, (ii) requirement of a company to disclose the name of the parties to which a contribution has been made. In addition, the Bill also proposes that contributions to parties will have to be made only through a cheque, bank draft, electronic means, or any other instrument notified by the central government.
Aadhaar mandatory for PAN and Income Tax
Amendments to the Finance Bill, 2017 make it mandatory for every person to quote their Aadhaar number after July 1, 2017 when: (i) applying for a Permanent Account Number (PAN), or (ii) filing their Income Tax returns. Persons who do not have an Aadhaar will be required to quote their Aadhaar enrolment number indicating that an application to obtain Aadhaar has been filed.
Every person holding a PAN on July 1, 2017 will be required to provide the authorities with his Aadhaar number by a date and in a manner notified by the central government. Failure to provide this number would result in the PAN being invalidated.
The Finance Bill, 2017 is making structural changes to some laws. Parliamentary committees allow for a forum for detailed scrutiny, deliberations and public consultation on proposed laws. The opportunity to build rigour into the law-making process is lost if such legislative changes are not examined by committees
[i] Madras Bar Association vs. Union of India, Transfer Case No. 150 of 2006, Supreme Court of India, September 25, 2014 (para 89).
As of May 11, 2020, there are 67,152 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in India. Since May 4, 24,619 new cases have been registered. Out of the confirmed cases so far, 20,917 patients have been cured/discharged and 2,206 have died. As the spread of COVID-19 has increased across the country, the central government has continued to announce several policy decisions to contain the spread, and support citizens and businesses who are being affected by the pandemic. In this blog post, we summarise some of the key measures taken by the central government in this regard between May 4 and May 11, 2020.
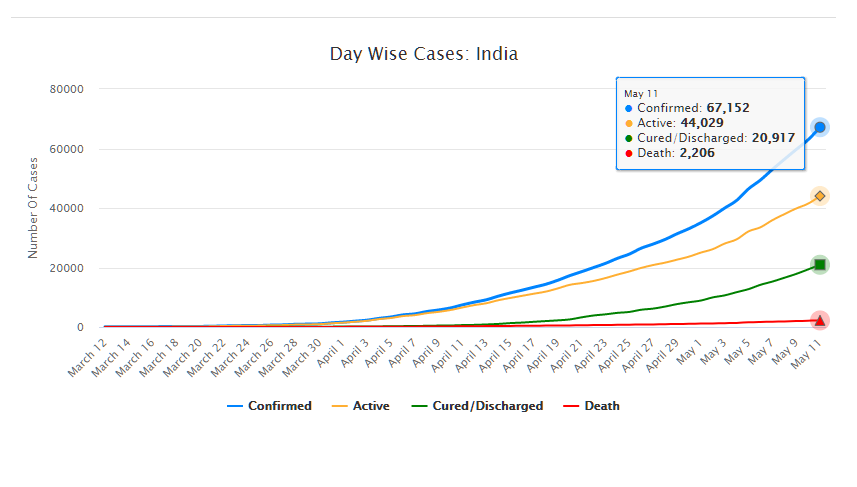
Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; PRS.
Industry
Relaxation of labour laws in some states
The Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Uttarakhand governments have passed notifications to increase maximum weekly work hours from 48 hours to 72 hours and daily work hours from 9 hours to 12 hours for certain factories. This was done to combat the shortage of labour caused by the lockdown. Further, some state governments stated that longer shifts would ensure a fewer number of workers in factories so as to allow for social distancing.
Madhya Pradesh has promulgated the Madhya Pradesh Labour Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020. The Ordinance exempts establishments with less than 100 workers from adhering to the Madhya Pradesh Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1961, which regulates the conditions of employment of workers. Further, it allows the state government to exempt any establishment or class of establishments from the Madhya Pradesh Shram Kalyan Nidhi Adhiniyam, 1982, which provides for the constitution of a welfare fund for labour.
The Uttar Pradesh government has published a draft Ordinance which exempts all factories and establishments engaged in manufacturing processes from all labour laws for a period of three years. Certain conditions will continue to apply with regard to payment of wages, safety, compensation and work hours, amongst others. However, labour laws providing for social security, industrial dispute resolution, trade unions, strikes, amongst others, will not apply under the Ordinance.
Financial aid
Central government signs an agreement with Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank for COVID-19 support
The central government and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a 500 million dollar agreement for the COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project. The project aims to help India respond to the COVID-19 pandemic and strengthen India’s public health system to manage future disease outbreaks. The project is being financed by the World Bank and AIIB in the amount of 1.5 billion dollars, of which one billion dollars is being provided by World Bank and 500 million dollars is being provided by AIIB. This financial support will be available to all states and union territories and will be used to address the needs of at-risk populations, medical personnel, and creating medical and testing facilities, amongst others. The project will be implemented by the National Health Mission, the National Center for Disease Control, and the Indian Council of Medical Research, under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Travel
Restarting of passenger travel by railways
Indian Railways plans to restart passenger trains from May 12 onwards. It will begin with 15 pairs of trains which will run from New Delhi station connecting Dibrugarh, Agartala, Howrah, Patna, Bilaspur, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar, Secunderabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Madgaon, Mumbai Central, Ahmedabad and Jammu Tawi. Booking for reservation in these trains will start at 4 pm on May 11. Thereafter, Indian Railways plans to start more services on new routes.
Return of Indians stranded abroad
The central government will facilitate the return of Indian nationals stranded abroad in a phased manner beginning on May 7. The travel will be arranged by aircraft and naval ships. The stranded Indians utilising the service will be required to pay for it. Medical screening of the passengers will be done before the flight. On reaching India, passengers will be required to download the Aarogya Setu app. Further, they will be quarantined by the concerned state government in either a hospital or a quarantine institution for 14 days on a payment basis. After quarantine, passengers will be tested for COVID-19 and further action will be taken based on the results.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.