
Applications for the LAMP Fellowship 2026-27 are closed. Shortlisted candidates will be asked to take an online test on January 4, 2026.
We wrote an FAQ on Parliamentary Privilege for IBN Live. See http://ibnlive.in.com/news/what-puri-bedi-are-guilty-of-parl-privilege-faqs/179977-37.html The full text is reproduced below. Several MPs have given breach of privilege notices against actor Om Puri and ex-policewoman Kiran Bedi for using "derogatory and defamatory" language against Members of Parliament. In light of this, we explain the concept of breach of privilege and contempt of Parliament. What is parliamentary privilege? Parliamentary privilege refers to rights and immunities enjoyed by Parliament as an institution and MPs in their individual capacity, without which they cannot discharge their functions as entrusted upon them by the Constitution. Are these parliamentary privileges defined under law? According to the Constitution, the powers, privileges and immunities of Parliament and MP's are to be defined by Parliament. No law has so far been enacted in this respect. In the absence of any such law, it continues to be governed by British Parliamentary conventions. What is breach of privilege? A breach of privilege is a violation of any of the privileges of MPs/Parliament. Among other things, any action 'casting reflections' on MPs, parliament or its committees; could be considered breach of privilege. This may include publishing of news items, editorials or statements made in newspaper/magazine/TV interviews or in public speeches. Have there been earlier cases of breach of privilege? There have been several such cases. In 1967, two people were held to be in contempt of Rajya Sabha, for having thrown leaflets from the visitors' gallery. In 1983, one person was held in breach for shouting slogans and throwing chappals from the visitors' gallery. What is the punishment in case of breach of privilege or contempt of the House? The house can ensure attendance of the offending person. The person can be given a warning and let go or be sent to prison as the case may be. In the case of throwing leaflets and chappal, the offending individuals were sentenced to simple imprisonment. In the 2007 case of breach of privilege against Ambassador Ronen Sen, the Lok Sabha Committee on privileges held that the phrase "headless chicken" was not used by Shri Sen in respect of MPs or politicians. No action was taken against him. In 2008, an editor of an Urdu weekly referred to the deputy chairman of Rajya Sabha as a "coward" attributing motives to a decision taken by him. The privileges committee held the editor guilty of breach of privilege. The committee instead of recommending punishment stated that, “it would be better if the House saves its own dignity by not giving undue importance to such irresponsible articles published with the sole intention of gaining cheap publicity.”
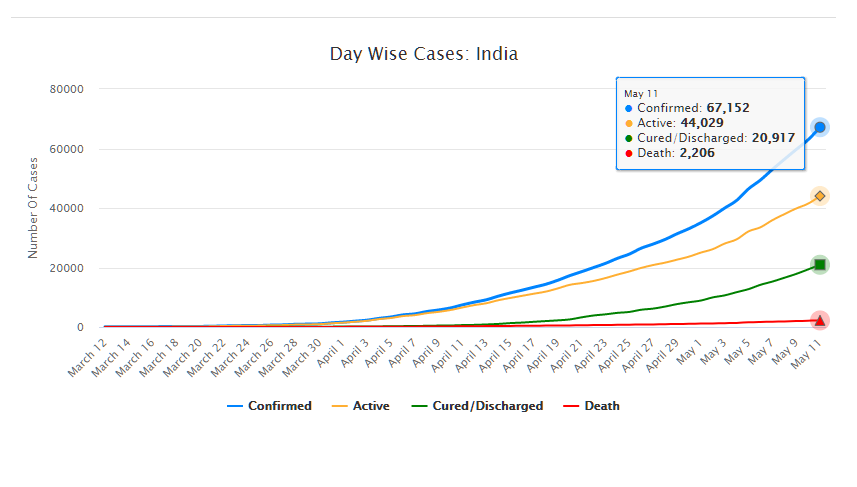
As of May 11, 2020, there are 67,152 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in India. Since May 4, 24,619 new cases have been registered. Out of the confirmed cases so far, 20,917 patients have been cured/discharged and 2,206 have died. As the spread of COVID-19 has increased across the country, the central government has continued to announce several policy decisions to contain the spread, and support citizens and businesses who are being affected by the pandemic. In this blog post, we summarise some of the key measures taken by the central government in this regard between May 4 and May 11, 2020.
Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; PRS.
Industry
Relaxation of labour laws in some states
The Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Uttarakhand governments have passed notifications to increase maximum weekly work hours from 48 hours to 72 hours and daily work hours from 9 hours to 12 hours for certain factories. This was done to combat the shortage of labour caused by the lockdown. Further, some state governments stated that longer shifts would ensure a fewer number of workers in factories so as to allow for social distancing.
Madhya Pradesh has promulgated the Madhya Pradesh Labour Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020. The Ordinance exempts establishments with less than 100 workers from adhering to the Madhya Pradesh Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1961, which regulates the conditions of employment of workers. Further, it allows the state government to exempt any establishment or class of establishments from the Madhya Pradesh Shram Kalyan Nidhi Adhiniyam, 1982, which provides for the constitution of a welfare fund for labour.
The Uttar Pradesh government has published a draft Ordinance which exempts all factories and establishments engaged in manufacturing processes from all labour laws for a period of three years. Certain conditions will continue to apply with regard to payment of wages, safety, compensation and work hours, amongst others. However, labour laws providing for social security, industrial dispute resolution, trade unions, strikes, amongst others, will not apply under the Ordinance.
Financial aid
Central government signs an agreement with Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank for COVID-19 support
The central government and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a 500 million dollar agreement for the COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project. The project aims to help India respond to the COVID-19 pandemic and strengthen India’s public health system to manage future disease outbreaks. The project is being financed by the World Bank and AIIB in the amount of 1.5 billion dollars, of which one billion dollars is being provided by World Bank and 500 million dollars is being provided by AIIB. This financial support will be available to all states and union territories and will be used to address the needs of at-risk populations, medical personnel, and creating medical and testing facilities, amongst others. The project will be implemented by the National Health Mission, the National Center for Disease Control, and the Indian Council of Medical Research, under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Travel
Restarting of passenger travel by railways
Indian Railways plans to restart passenger trains from May 12 onwards. It will begin with 15 pairs of trains which will run from New Delhi station connecting Dibrugarh, Agartala, Howrah, Patna, Bilaspur, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar, Secunderabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Madgaon, Mumbai Central, Ahmedabad and Jammu Tawi. Booking for reservation in these trains will start at 4 pm on May 11. Thereafter, Indian Railways plans to start more services on new routes.
Return of Indians stranded abroad
The central government will facilitate the return of Indian nationals stranded abroad in a phased manner beginning on May 7. The travel will be arranged by aircraft and naval ships. The stranded Indians utilising the service will be required to pay for it. Medical screening of the passengers will be done before the flight. On reaching India, passengers will be required to download the Aarogya Setu app. Further, they will be quarantined by the concerned state government in either a hospital or a quarantine institution for 14 days on a payment basis. After quarantine, passengers will be tested for COVID-19 and further action will be taken based on the results.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.