
The Department of Land Resources in the Ministry of Rural Development has released a draft version of The Land Titling Bill, 2011 on its website. This draft is a major revision of the original draft Bill released in 2010. Public comments on this draft are invited before June 24, 2011. A copy of the draft can be found here. The Bill provides for the registration of all immovable property to establish a system of conclusive, electronically recorded titles. It also provides for a mechanism to invite objections and for the resolution of disputes through special tribunals. The property record will be considered as conclusive ownership by the person mentioned. This will help resolve uncertainties in property transactions. Given that land is a state subject, the Bill is meant to be a model law for adoption by the states individually. The framework of the bill is explained below. I. Land Titling Authority and Preparation of Records The Bill establishes a Land Titling Authority at the State level. The Authority’s task is to prepare a record of all immovable properties in its jurisdiction. These records will contain (a) survey data of boundaries of each property; (b) a unique identification number for each property, which may be linked to a UID number; (c) any record created by an officer of the state or UT government authorised by the laws of that state to make such records; and (d) a record of Title over each property. II. Title Registration Officer and Registration Process The Bill provides for the government to create Title Registration Offices at various places, and for a Title Registration Officer (TRO) to function under the supervision of the Land Titling Authority. The TRO will have powers of a civil court and is charged with the task of creating e a Register of Titles. Steps for the registering of titles include: (a) notification of available land records data by the TRO, (b) invitation to persons with interest in such properties to make objections to the data, and (c) registration of properties by the TRO for which no dispute is brought to his notice in writing. In the case the absoluteness of the title to a property is disputed, the TRO will make an entry into the Register of Titles to that effect and refer the case to the District Land Titling Tribunal (discussed below) III. District Land Titling Tribunal and State Land Titling Appellate Tribunal The Bill proposes to set up a District Land Titling Tribunal, consisting of one or more serving officers not below the rank of Joint Collector / Sub Divisional Magistrate of the District. The government may also establish one or more State Land Titling Appellate Tribunals, to be presided over by serving Judicial Officers in the rank of District Judge. Revisions to the orders of the State Land Titling Appellate Tribunal may be made by a Special Bench of the High Court. The Bill bars civil courts from having jurisdiction to entertain proceedings in respect to matters that the TRO, District Land Titling Tribunal, and State Land Titling Appellate Tribunal are empowered to determine. IV. Completion of Records and Notification When preparation of the Record for whole or part of a specific are is complete, it will be notified. Any person aggrieved by the notified entry in the Register of Titles may file an objection before the District Land Titling Tribunal within three years of the notification. Additionally, the person may file an application with the TRO for an entry to be made in the Register of Titles. The TRO shall do so when the application has been admitted to the Tribunal. Minor errors in the Title of Registers can be rectified through an application to the TRO. V. Register of Titles After completion of records is notified by the Authority, the Register of Titles is prepared and maintained by the Authority. For each property, the Register will include: (a) general description, map, and locational details of the immovable property; (b) descriptive data such as a unique identification number, plot number, total area, built up and vacant area, address, site area, and undivided share in the land; (c) detail of survey entry, provisional title record, conclusive title record and status, mortgage, charges, other rights and interests in the property; (d) details of transfer of the property and past transactions; and (e) disputes pertaining to the property. Entries in the Register of Titles will serve as conclusive evidence of ownership. These entries shall be maintained in electronic form, indemnified, and kept in the public domain.
As of May 11, 2020, there are 67,152 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in India. Since May 4, 24,619 new cases have been registered. Out of the confirmed cases so far, 20,917 patients have been cured/discharged and 2,206 have died. As the spread of COVID-19 has increased across the country, the central government has continued to announce several policy decisions to contain the spread, and support citizens and businesses who are being affected by the pandemic. In this blog post, we summarise some of the key measures taken by the central government in this regard between May 4 and May 11, 2020.
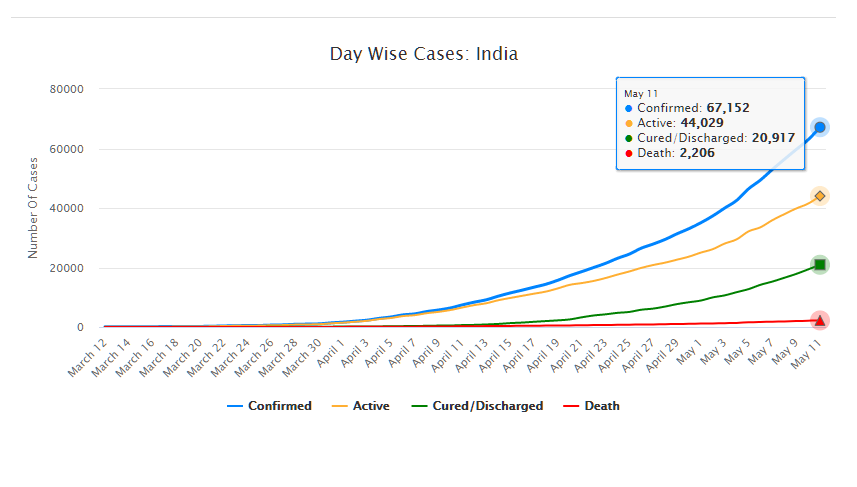
Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; PRS.
Industry
Relaxation of labour laws in some states
The Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Uttarakhand governments have passed notifications to increase maximum weekly work hours from 48 hours to 72 hours and daily work hours from 9 hours to 12 hours for certain factories. This was done to combat the shortage of labour caused by the lockdown. Further, some state governments stated that longer shifts would ensure a fewer number of workers in factories so as to allow for social distancing.
Madhya Pradesh has promulgated the Madhya Pradesh Labour Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020. The Ordinance exempts establishments with less than 100 workers from adhering to the Madhya Pradesh Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1961, which regulates the conditions of employment of workers. Further, it allows the state government to exempt any establishment or class of establishments from the Madhya Pradesh Shram Kalyan Nidhi Adhiniyam, 1982, which provides for the constitution of a welfare fund for labour.
The Uttar Pradesh government has published a draft Ordinance which exempts all factories and establishments engaged in manufacturing processes from all labour laws for a period of three years. Certain conditions will continue to apply with regard to payment of wages, safety, compensation and work hours, amongst others. However, labour laws providing for social security, industrial dispute resolution, trade unions, strikes, amongst others, will not apply under the Ordinance.
Financial aid
Central government signs an agreement with Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank for COVID-19 support
The central government and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a 500 million dollar agreement for the COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project. The project aims to help India respond to the COVID-19 pandemic and strengthen India’s public health system to manage future disease outbreaks. The project is being financed by the World Bank and AIIB in the amount of 1.5 billion dollars, of which one billion dollars is being provided by World Bank and 500 million dollars is being provided by AIIB. This financial support will be available to all states and union territories and will be used to address the needs of at-risk populations, medical personnel, and creating medical and testing facilities, amongst others. The project will be implemented by the National Health Mission, the National Center for Disease Control, and the Indian Council of Medical Research, under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Travel
Restarting of passenger travel by railways
Indian Railways plans to restart passenger trains from May 12 onwards. It will begin with 15 pairs of trains which will run from New Delhi station connecting Dibrugarh, Agartala, Howrah, Patna, Bilaspur, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar, Secunderabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Madgaon, Mumbai Central, Ahmedabad and Jammu Tawi. Booking for reservation in these trains will start at 4 pm on May 11. Thereafter, Indian Railways plans to start more services on new routes.
Return of Indians stranded abroad
The central government will facilitate the return of Indian nationals stranded abroad in a phased manner beginning on May 7. The travel will be arranged by aircraft and naval ships. The stranded Indians utilising the service will be required to pay for it. Medical screening of the passengers will be done before the flight. On reaching India, passengers will be required to download the Aarogya Setu app. Further, they will be quarantined by the concerned state government in either a hospital or a quarantine institution for 14 days on a payment basis. After quarantine, passengers will be tested for COVID-19 and further action will be taken based on the results.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.