
The budget session of Parliament every year starts with the President’s Address to both Houses. In this speech, the President highlights the government’s achievements and legislative activities in the last year, and announces its agenda for the upcoming year. The address is followed by a motion of thanks that is moved in each House by ruling party MPs. This is followed by a discussion on the address and concludes with the Prime Minister replying to the points raised during the discussion.
Today, the Budget Session 2019 commenced with the President, Mr. Ram Nath Kovind addressing a joint sitting of Parliament. In his speech, he highlighted some of the objectives that the government has realised in the past year. The President also highlighted the progress made by the government under various development schemes such as the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana, and the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana.
Given that today’s address comes at the end of this government’s term, we examine the status of some key policy initiatives announced by the current government, that have been highlighted in speeches made in the past five years.
|
Policy priority stated in President’s Addresses 2014-2018 |
Current Status |
|
Economy and Finance |
|
|
Despite a global economic downturn, the Indian economy has remained on a high growth trajectory.
|
|
|
Measures to deal with corruption, black money and counterfeit currency will be introduced
|
|
|
To promote the concept of cooperative federalism through One Nation-One Tax and One Nation-One Market, the government introduced the Goods and Services Tax |
|
|
Agriculture |
|
|
Agriculture is the main source of livelihood for a majority of people. For holistic development of the agricultural sector, the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana was launched in 2016 |
|
|
Employment and Entrepreneurship |
|
|
The government has continuously worked for reforms of labour laws. Minimum wages have increased by more than 40%
|
|
|
Infrastructure |
|
|
Cities are the engines of economic growth. The Smart City programme was initiated to build modern amenities and infrastructure.
|
|
|
All rural habitations will be connected with all-weather roads. So far, 73,000 kilometres of roads have been laid in rural areas.
|
|
|
Housing is a fundamental right. All households shall have a dwelling unit under the Mission Housing for All by 2022.
|
|
|
Health and Sanitation |
|
|
Poor sanitation weakens the economic wherewithal of a poor household. The Swachh Bharat Abhiyan aims to ensure health and sanitation. |
|
|
The government is committed to providing affordable and accessible healthcare to all its citizens, particularly the vulnerable groups. |
|
Source: President’s Addresses 2014-2018; PRS.
For important highlights from the President’s address in 2019, please see here. For a deeper analysis of the status of implementation of the announcements made in the President’s addresses from 2014 to 2018, please see here.
[i] “Press Note on First Advance Estimates of National Income: 2018-19”, Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation, Press Information Bureau, http://www.mospi.gov.in/sites/default/files/press_release/Presss%20note%20for%20first%20advance%20estimates%202018-19.pdf.
[ii] “Second Advance Estimates of National Income, 2017-18”, Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation, Press Information Bureau, http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=176847
[iii] “Second Advance Estimates of National Income, 2016-17”, Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation, Press Information Bureau, http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=158734
[iv] Overview-Monetary Policy, Reserve Bank of India, https://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/FS_Overview.aspx?fn=2752.
[v] “Foreign Exchange Reserves,” Reserve Bank of India, January 25, 2019, https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/WSSView.aspx?Id=22729.
[vi] RBI Database, https://dbie.rbi.org.in/DBIE/dbie.rbi?site=home.
[vii] Table No. 160, Handbook of Statistics on the Indian Economy, Reserve Bank of India, https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/AnnualPublications.aspx?head =Handbook%20of%20Statistics%20on%20Indian%20Economy
[viii] Lok Sabha Unstarred Question No. 1319, Ministry of Finance, December 22, 2017, http://164.100.47.194/Loksabha/Questions/QResult15.aspx?qref=59329&lsno=16.
[ix] “The Fugitive Economic Offenders Bill, 2018”, PRS Legislative Research, March 16, 2018, http://www.prsindia.org/sites/default/files/bill_files/Fugitive%20Economic%20Offenders%20Bill%20-%20Bill%20Summary.pdf.
[x] “The Prevention of Corruption (Amendment) Bill”, PRS Legislative Research, February 12, 2014, http://www.prsindia.org/sites/default/files/bill_files/Bill_Summary-_Prevention_of_Corruption_1.pdf.
[xi] “GST roll-out – Complete transformation of the Indirect Taxation Landscape; Some minute details of how it happened, Ministry of Finance”, Press Information Bureau, June 30, 2017, http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=167023.
[xii] Lok Sabha Unstarred Question No. 17, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, December 11, 2018, http://164.100.47.190/loksabhaquestions/annex/16/AS17.pdf.
[xiii] “Year End Review, Ministry of Labour and Employment”, December 18, 2017, http://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=1512998.
[xiv] Rate of Minimum Wages, Ministry of Labour and Employment, March 1 2017, https://labour.gov.in/sites/default/files/MX-M452N_20170518_132440.pdf.
[xv] Gazette Number 173, Ministry of Labour and Employment, January 19, 2017, Gazette of India, http://egazette.nic.in/WriteReadData/2017/173724.pdf.
[xvi] “Union Cabinet approves Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation and Smart Cities Mission to drive economic growth and foster inclusive urban development”, Press Information Bureau, April 29, 2015, http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=119925.
[xvii] “Shillong (Meghalaya) gets selected as the 100th Smart City”, Ministry of Housing and Urban Poverty Alleviation, Press Information Bureau, June 20, 2018, http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=180063
[xviii] “Year Ender- Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs-2018”, Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Press Information Bureau, December 31, 2018, http://pib.nic.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=1557895.
[xix] PMGSY Guidelines, Ministry of Rural Development, last accessed on October 23, 2018. http://pmgsy.nic.in/.
[xx] “Implementation of PMGSY”, Ministry of Rural Development, Press Information Bureau, December 27, 2018, http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=186837.
[xxi] Online Management, Monitoring and Accounting System (OMMAS), Pradhan Mantri, Gram Sadak Yojana, last accessed on October 23, 2018, http://omms.nic.in/Home/CitizenPage/#.
[xxii] High Level Physical Progress Report, PMAYG, Ministry of Rural Development, last accessed on January 25, 2019, https://rhreporting.nic.in/netiay/PhysicalProgressReport/physicalprogressreport.aspx
[xxiii] “Year Ender-6-PMAY-Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, 2018”, Press Information Bureau, December 27, 2018, http://pib.nic.in/PressReleseDetail.aspx?PRID=1557462.
[xxiv] “Swachh Bharat Mission needs to become a Jan Andolan with participation from every stakeholder: Hardeep Puri, 1,789 Cities have been declared ODF conference on PPP model for waste to energy projects”, Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Press Information Bureau, November 30, 2017, http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=173995.
[xxv] “PM launches Swachh Bharat Abhiyaan”, Prime Minister’s Office, Press Information Bureau, October 2, 2014, http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=110247.
[xxvi] “Individual Household Latrine Application”, Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, last accessed on January 30, 2019, http://swachhbharaturban.gov.in/ihhl/RPTApplicationSummary.aspx.
[xxvii] “Individual Household Latrine Application”, Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, last accessed on January 30, 2019, http://swachhbharaturban.gov.in/ihhl/RPTApplicationSummary.aspx.
[xxviii] Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin), Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation, last accessed on January 30, 2019, https://sbm.gov.in/sbmdashboard/Default.aspx.
[xxix] “Ayushman Bharat for a new India -2022, announced”, Ministry of Finance, Press Information Bureau, February 1, 2018,s http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=176049
[xxx] About NHA, Ayushmaan Bharat, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, https://www.pmjay.gov.in/about-nha.
[xxxi] “Ayushman Bharat –Pradhan Mantri Jan AarogyaYojana (AB-PMJAY) to be launched by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi in Ranchi, Jharkahnd on September 23, 2018”, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Press Information Bureau, September 22, 2018, http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=183624.
[xxxii] National Health Accounts, estimates for 2014-15 Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, https://mohfw.gov.in/newshighlights/national-health-accounts-estimates-india-2014-15.
As of May 11, 2020, there are 67,152 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in India. Since May 4, 24,619 new cases have been registered. Out of the confirmed cases so far, 20,917 patients have been cured/discharged and 2,206 have died. As the spread of COVID-19 has increased across the country, the central government has continued to announce several policy decisions to contain the spread, and support citizens and businesses who are being affected by the pandemic. In this blog post, we summarise some of the key measures taken by the central government in this regard between May 4 and May 11, 2020.
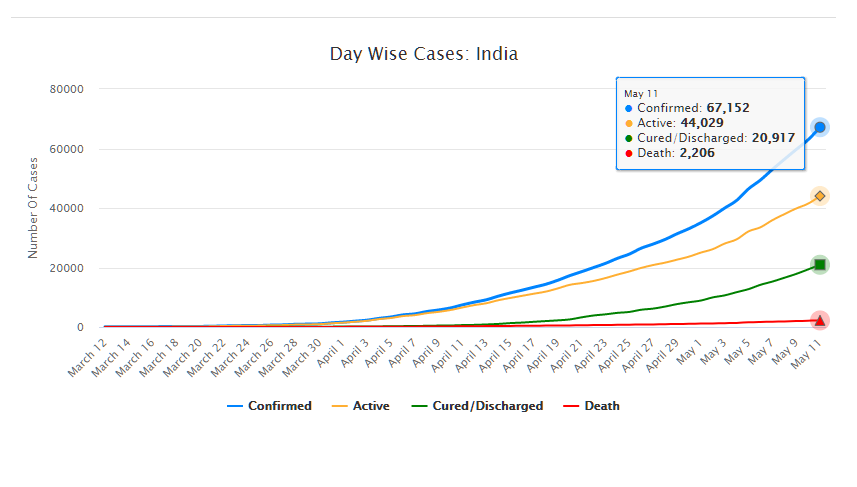
Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; PRS.
Industry
Relaxation of labour laws in some states
The Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Uttarakhand governments have passed notifications to increase maximum weekly work hours from 48 hours to 72 hours and daily work hours from 9 hours to 12 hours for certain factories. This was done to combat the shortage of labour caused by the lockdown. Further, some state governments stated that longer shifts would ensure a fewer number of workers in factories so as to allow for social distancing.
Madhya Pradesh has promulgated the Madhya Pradesh Labour Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020. The Ordinance exempts establishments with less than 100 workers from adhering to the Madhya Pradesh Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1961, which regulates the conditions of employment of workers. Further, it allows the state government to exempt any establishment or class of establishments from the Madhya Pradesh Shram Kalyan Nidhi Adhiniyam, 1982, which provides for the constitution of a welfare fund for labour.
The Uttar Pradesh government has published a draft Ordinance which exempts all factories and establishments engaged in manufacturing processes from all labour laws for a period of three years. Certain conditions will continue to apply with regard to payment of wages, safety, compensation and work hours, amongst others. However, labour laws providing for social security, industrial dispute resolution, trade unions, strikes, amongst others, will not apply under the Ordinance.
Financial aid
Central government signs an agreement with Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank for COVID-19 support
The central government and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a 500 million dollar agreement for the COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project. The project aims to help India respond to the COVID-19 pandemic and strengthen India’s public health system to manage future disease outbreaks. The project is being financed by the World Bank and AIIB in the amount of 1.5 billion dollars, of which one billion dollars is being provided by World Bank and 500 million dollars is being provided by AIIB. This financial support will be available to all states and union territories and will be used to address the needs of at-risk populations, medical personnel, and creating medical and testing facilities, amongst others. The project will be implemented by the National Health Mission, the National Center for Disease Control, and the Indian Council of Medical Research, under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Travel
Restarting of passenger travel by railways
Indian Railways plans to restart passenger trains from May 12 onwards. It will begin with 15 pairs of trains which will run from New Delhi station connecting Dibrugarh, Agartala, Howrah, Patna, Bilaspur, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar, Secunderabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Madgaon, Mumbai Central, Ahmedabad and Jammu Tawi. Booking for reservation in these trains will start at 4 pm on May 11. Thereafter, Indian Railways plans to start more services on new routes.
Return of Indians stranded abroad
The central government will facilitate the return of Indian nationals stranded abroad in a phased manner beginning on May 7. The travel will be arranged by aircraft and naval ships. The stranded Indians utilising the service will be required to pay for it. Medical screening of the passengers will be done before the flight. On reaching India, passengers will be required to download the Aarogya Setu app. Further, they will be quarantined by the concerned state government in either a hospital or a quarantine institution for 14 days on a payment basis. After quarantine, passengers will be tested for COVID-19 and further action will be taken based on the results.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.