
Speaker Meira Kumar has urged political parties to arrive at a consensus on the women’s reservation bill. The 2008 Bill has the following main features. 1. It reserves one-third of all seats in Lok Sabha and Legislative Assemblies within each state for women. 2. There is quota-within-quota for SCs, STs and Anglo-Indians. 3. The reserved seats will be rotated after each general elections – thus after a cycle of three elections, all constituencies would have been reserved once. This reservation will be operational for 15 years. This Bill has had a chequered history. A similar Bill was introduced in 1996, 1998 and 1999 – all of which lapsed after the dissolution of the respective Lok Sabhas. A Joint Parliamentary Committee chaired by Geeta Mukherjee examined the 1996 Bill and made seven recommendations. Five of these have been included in the latest 2008 Bill. These are (i) reservation for a period of 15 years; (ii) including sub-reservation for Anglo Indians; (iii) including reservation in cases where the state has less than three seats in Lok Sabha (or less than three seats for SCs/STs); (iv) including reservation for the Delhi assembly; and (v) changing “not less than one-third” to “as nearly as may be, one-third”. Two of the recommendations are not incorporated in the 2008 Bill. The first is for reserving seats in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils. The second is for sub-reservation for OBC women after the Constitution extends reservation to OBCs. The 2008 Bill was referred to the Standing Committee on Law and Justice. This Committee failed to reach a consensus in its final report. The Committee has recommendedthat the Bill “be passed in Parliament and put in action without further delay. Two members of the Committee, Virender Bhatia and Shailendra Kumar (both belonging to the Samajwadi Party) dissented stating that they were not against providing reservation to women but disagreed with the way this Bill was drafted. They had three recommendations: (i) every political party must distribute 20% of its tickets to women; (ii) even in the current form, reservation should not exceed 20% of seats; and (iii) there should be a quota for women belonging to OBCs and minorities. The Standing committee considered two other methods of increasing representation. One suggestion (part of election commission recommendations) was to requite political parties to nominate women for a minimum percentage of seats. The committee felt that parties could bypass the spirit of the law by nominating women to losing seats. The second recommendation was to create dual member constituencies, with women filling one of the two seats from those constituencies. The Committee believed that this move could “result in women being reduced to a subservient status, which will defeat the very purpose of the Bill”. It is interesting to note that the Committee did not reject the two recommendations of the Geeta Mukherjee Committee that are not reflected in the Bill. The Committee concluded that the issue of reservations to Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils needs to be examined thoroughly as the upper Houses play an equally important role under the Constitution. Incidentally, it is not possible to reserve seats in Rajya Sabha given the current system of elections to that house (see Appendix below). On the issue of reservations to OBC women, the Committee said that “all other issues may be considered at an appropriate time by Government without any further delay at the present time in the passage of the Bill”. Though the Bill does not have a consensus – it has been opposed by SP, RJD and JD(U) – most parties have publicly expressed their support for it. The government will likely not find it difficult to muster two-third support in each House of Parliament were the Bill be taken up for consideration and passing. It would be interesting to see whether the Bill is brought before Parliament in the upcoming Budget Session. Appendix: Impossibility of Reservation in Rajya Sabha Article 80of the Constitution specifies that members of state assemblies will elect Rajya Sabha MPs through single transferable vote. This implies that the votes are first allocated to the most preferred candidate, and then to the next preferred candidate, and so on. This system cannot accommodate the principle of reserving a certain number of seats for a particular group. Currently, Rajya Sabha does not have reservation for SCs and STs. Therefore, any system that provides reservation in Rajya Sabha implies that the Constitution must be amended to jettison the Single Transferable Vote system.
As of May 11, 2020, there are 67,152 confirmed cases of COVID-19 in India. Since May 4, 24,619 new cases have been registered. Out of the confirmed cases so far, 20,917 patients have been cured/discharged and 2,206 have died. As the spread of COVID-19 has increased across the country, the central government has continued to announce several policy decisions to contain the spread, and support citizens and businesses who are being affected by the pandemic. In this blog post, we summarise some of the key measures taken by the central government in this regard between May 4 and May 11, 2020.
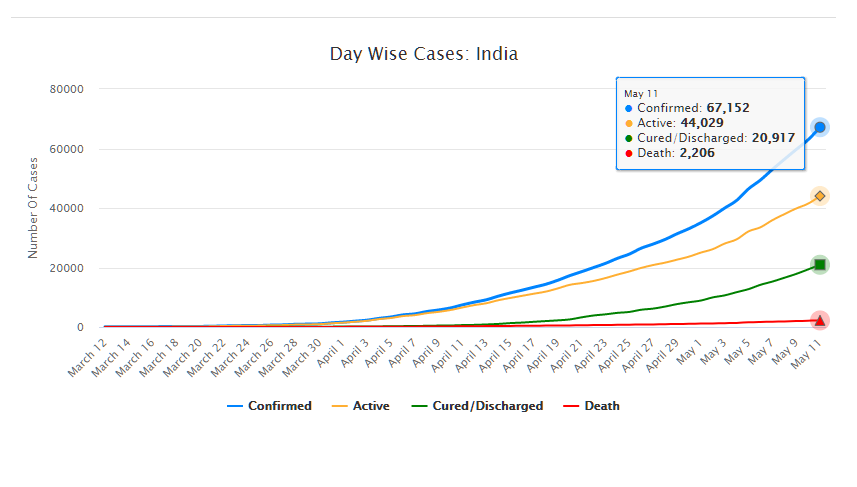
Source: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; PRS.
Industry
Relaxation of labour laws in some states
The Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Uttarakhand governments have passed notifications to increase maximum weekly work hours from 48 hours to 72 hours and daily work hours from 9 hours to 12 hours for certain factories. This was done to combat the shortage of labour caused by the lockdown. Further, some state governments stated that longer shifts would ensure a fewer number of workers in factories so as to allow for social distancing.
Madhya Pradesh has promulgated the Madhya Pradesh Labour Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020. The Ordinance exempts establishments with less than 100 workers from adhering to the Madhya Pradesh Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1961, which regulates the conditions of employment of workers. Further, it allows the state government to exempt any establishment or class of establishments from the Madhya Pradesh Shram Kalyan Nidhi Adhiniyam, 1982, which provides for the constitution of a welfare fund for labour.
The Uttar Pradesh government has published a draft Ordinance which exempts all factories and establishments engaged in manufacturing processes from all labour laws for a period of three years. Certain conditions will continue to apply with regard to payment of wages, safety, compensation and work hours, amongst others. However, labour laws providing for social security, industrial dispute resolution, trade unions, strikes, amongst others, will not apply under the Ordinance.
Financial aid
Central government signs an agreement with Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank for COVID-19 support
The central government and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a 500 million dollar agreement for the COVID-19 Emergency Response and Health Systems Preparedness Project. The project aims to help India respond to the COVID-19 pandemic and strengthen India’s public health system to manage future disease outbreaks. The project is being financed by the World Bank and AIIB in the amount of 1.5 billion dollars, of which one billion dollars is being provided by World Bank and 500 million dollars is being provided by AIIB. This financial support will be available to all states and union territories and will be used to address the needs of at-risk populations, medical personnel, and creating medical and testing facilities, amongst others. The project will be implemented by the National Health Mission, the National Center for Disease Control, and the Indian Council of Medical Research, under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Travel
Restarting of passenger travel by railways
Indian Railways plans to restart passenger trains from May 12 onwards. It will begin with 15 pairs of trains which will run from New Delhi station connecting Dibrugarh, Agartala, Howrah, Patna, Bilaspur, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar, Secunderabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Madgaon, Mumbai Central, Ahmedabad and Jammu Tawi. Booking for reservation in these trains will start at 4 pm on May 11. Thereafter, Indian Railways plans to start more services on new routes.
Return of Indians stranded abroad
The central government will facilitate the return of Indian nationals stranded abroad in a phased manner beginning on May 7. The travel will be arranged by aircraft and naval ships. The stranded Indians utilising the service will be required to pay for it. Medical screening of the passengers will be done before the flight. On reaching India, passengers will be required to download the Aarogya Setu app. Further, they will be quarantined by the concerned state government in either a hospital or a quarantine institution for 14 days on a payment basis. After quarantine, passengers will be tested for COVID-19 and further action will be taken based on the results.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.