
The Budget session 2013 commenced with the President, Pranab Mukherjee, addressing Parliament on February 21, 2013. The address is a statement of the policy of the government. Yesterday a Motion of Thanks was moved in the Lok Sabha and a detailed discussion took place on the President’s address. (The significance of the President’s speech has been discussed in an article published in the Indian Express.) Below are some legislative and policy items from the agenda of the central government outlined in the speech.
Legislative and policyagenda outlined in President’s addresses between 2009-2012 and their status
|
Legislation/Policy |
Status |
|
Legislations mentioned in the President’s Address between 2009-12 |
|
| To be introduced | |
| Goods and Services Tax | Constitutional Amendment Bill introduced |
| The National Food Security Bill | Introduced |
| Amend the Land Acquisition Act and enact the Rehabilitation and Resettlement Bill | Introduced |
| Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention Prohibition and Redressal) Bill | Passed |
| The Whistleblower Bill | Pending |
| The Judicial Standards and Accountability Bill | Pending |
| The Lokpal and Lokayuktas Bill | Pending |
| A model Public Services Law (to cover officials providing important social services and commits them to their duties) | Two bills introduced: the Electronic Services Delivery Bill and the Citizen’s Charter Bill |
| The Right to Free and Compulsory Education Bill | Passed |
| The National Council for Higher Education Bill | Introduced |
| Foreign Educational Institutions Bill | Introduced |
| Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Bill | Passed |
| The Women’s Reservation Bill | Pending |
| The Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Bill | Introduced |
| The Public Procurement Bill | Introduced |
| The General Anti-Avoidance Rules | Scheduled for 2016[1] |
| Amend of RTI Act (to provide for disclosure by government in all non-strategic areas) | To be introduced |
|
Policy items mentioned in the President’s Addresses between 2009-2012 |
|
| National Mission for Female Literacy – all women to be literate by 2013-14 | National Literacy Mission recast in September 2009 to focus on female literacy; as per 2011 census the female literacy rate in India is 65.46%[2] |
| Disposal of remaining claims in 2010 under the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers Act | As on February 28, 2010, 27.16 lakh claims had been filed, 7.59 lakh titles had been distributed and 36,000 titles were ready for distribution;[3] as on July 31, 2012, the number of claims filed for the recognition of forest rights and titles distributed are 32.28 lakh and 12.68 lakh respectively[4] |
| Introduction of Minimum Support Price (MSP) for Minor Forest Produce (MFP) being considered | Based on the recommendations of the Committee constituted by Ministry of Panchayati Raj to look into aspects of MSP, Value addition and marketing of MFP in Fifth Schedule Areas, a Central Sector Scheme of MSP for MFP has been contemplated[5] |
| Voting rights for Indian citizens living abroad | Bill passed; NRIs can vote at the place of residence mentioned in their passport |
| 12th Plan target growth 9% with 4% growth for the agricultural sector | GDP grew by 5.4% and the agriculture sector by 1.8% in the first half of the current fiscal year (2012-13) |
| Establish national investment and manufacturing zones to promote growth in manufacturing | Under the National Manufacturing Policy, 12 National Investment and Manufacturing Zones are notified, 8 of them along the Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor and 4 others at Nagpur, Tumkur, Chittor and Medak |
| Strengthening public accountability of flagship programmes by the creation of an Independent Evaluation Office. | Government has approved setting up of an Independent Evaluation Office and the Governing Board will be chaired by Deputy Chairman, Planning Commission |
| Unique Identity Card scheme to be implemented by 2011-12 | Bill to give statutory status pending in Parliament; enrollment until February 2013 is approximately 28 crore[6] |
| Establishment of National Counter-Terrorism Centre | Proposed launch of NCTC in March 2011 on hold as consultation with states is on; meeting held by the union government with the Chief Ministers of all the States in May 2012 |
| Conversion of analog cable TV system to digital by December 2014 | Government has implemented the first phase of digitization in Kolkata, Delhi, Chennai and Mumbai; by March 31, 2013, 38 cities with a population of more than one million will be covered |
| A roadmap for judicial reform to be outlined by the end of 2009 and implemented in a time-bound manner | Vision statement formulated in 2009 outlining road map for improving justice delivery and legal reforms and steps to reduce pendency in Courts; setting up of a National Mission for the Delivery of Justice and Legal Reforms to improve court administration and reduce pendency was approved in June 2011 |
*Introduced means introduced in one House; Pending means passed by one House and pending in the other House; Passed means passed by both Houses of Parliament.
[1] “Major Recommendations of Expert Committee on GAAR Accepted”, Press Information Bureau, Ministry of Finance, January 14, 2013.
[2] Lok Sabha, Starred Question No. 175, December 5, 2012, Ministry of Human Resource Development.
[3] Lok Sabha, Unstarred Question No. 2672, March 12, 2010, Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
[4] Lok Sabha, Starred Question No. 108, August 17, 2012, Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
[5] “PM approves Constitution of National Council for Senior Citizens”, Press Information Bureau, February 1, 2012, Prime Minister’s Office.
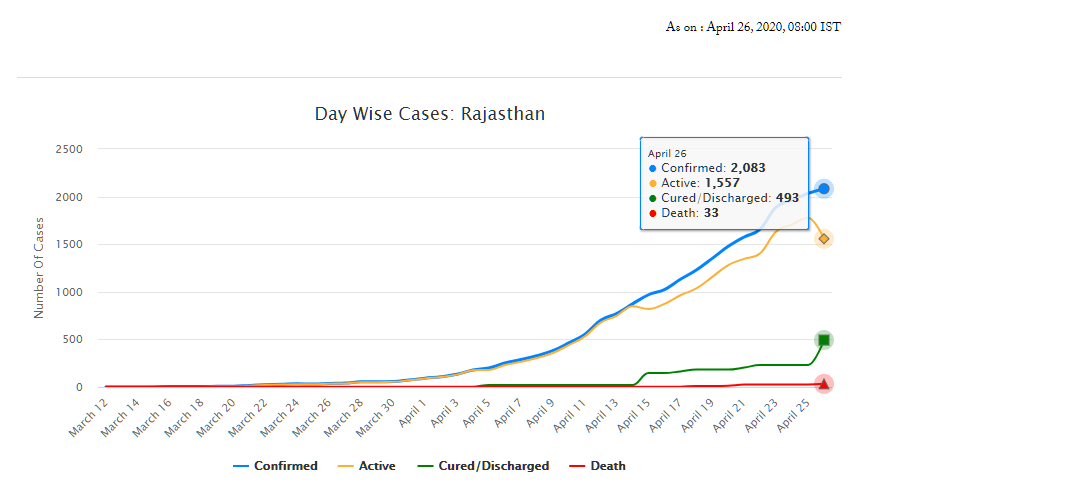
As of April 26, Rajasthan has 2,083 confirmed cases of COVID-19 (fifth highest in the country), of which 493 have recovered and 33 have died. On March 18, the Rajasthan government had declared a state-wide curfew till March 31, to check the spread of the disease. A nation-wide lockdown has also been in place since March 25 and is currently, extended up to May 3. The state has announced several policy decisions to prevent the spread of the virus and provide relief for those affected by it. This blog summarises the key policy measures taken by the Government of Rajasthan in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Early measures for containment
Between late January and early February, Rajasthan Government’s measures were aimed towards identification, screening and testing, and constant monitoring of passenger arrivals from China. Instructions were also issued to district health officials for various prevention, treatment, & control related activities, such as (i) mandatory 28-day home isolation for all travellers from China, (ii) running awareness campaigns, and (iii) ensuring adequate supplies of Personal Protection Equipments (PPEs). Some of the other measures, taken prior to the state-wide lockdown, are summarised below:
Administrative measures
The government announced the formation of Rapid Response Teams (RRTs), at the medical college-level and at district-level on March 3 and 5, respectively.
The District Collector was appointed as the Nodal Officer for all COVID-19 containment activities. Control Rooms were to be opened at all Sub-divisional offices. The concerned officers were also directed to strengthen information dissemination mechanisms and tackle the menace of fake news.
Directives were issued on March 11 to rural health workers/officials to report for duty on Gazetted holidays. Further, government departments were shut down between March 22 and March 31. Only essential departments such as Health Services were allowed to function on a rotation basis at 50% capacity and special / emergency leaves were permitted.
Travel and Movement
Air travellers were to undergo 14-day home isolation and were also required to provide an undertaking for the same. Besides, those violating the mandated isolation/quarantine were liable to be punished under Section. 188 of the Indian Penal Code. Penalties are imposed under this section on persons for the willful violation of orders that have been duly passed by a public servant.
All institutions and establishments, such as (i) educational institutions, theatres, and gyms, (ii) anganwadis, (iii) bars, discos, libraries, restaurants etc, (iv) museums and tourist places, were directed to be shut down till March 31.
The daily Jan Sunwai at the Chief Minister’s residence was cancelled until further notice. Various government offices were directed to shut down and exams of schools and colleges were postponed.
On March 24, the government issued a state-wide ban on the movement of private vehicles till March 31.
Health Measures
Advisories regarding prevention and control measures were issued to: (i) District Collectors, regarding sample collection and transportation, hotels, and preparedness of hospitals, (ii) Police department, to stop using breath analysers, (iii) Private hospitals, regarding preparedness and monitoring activities, and (iv) Temple trusts, to disinfect their premises with chemicals.
The government issued Standard Operating Procedures for conducting mock drills in emergency response handling of COVID-19 cases. Training and capacity building measures were also initiated for (i) Railways, Army personnel etc and (ii) ASHA workers, through video conferencing.
A model micro-plan for containing local transmission of COVID was released. Key features of the plan include: (i) identification and mapping of affected areas, (ii) activities for prevention control, surveillance, and contact tracing, (iii) human resource management, including roles and responsibilities, (iv) various infrastructural and logistical support, such as hospitals, labs etc, and (v) communication and data management.
Resource Management: Private hospitals and medical colleges were instructed to reserve 25 % of beds for COVID-19 patients. They were also instructed to utilise faculty from the departments of Preventive and Social Medicine to conduct health education and awareness activities.
Over 6000 Students of nursing schools were employed in assisting the health department to conduct screening activities being conducted at public places, railways stations, bus stands etc.
Further, the government issued guidelines to ensure the rational use of PPEs.
Welfare Measures
The government announced financial assistance, in the form of encouragement grants, to health professionals engaged in treating COVID-19 patients.
Steps were also taken by the government to ensure speedy disbursal of pensions for February and March.
The government also initiated the replacement of the biometric authentication with an OTP process for distribution of ration via the Public Distribution System (PDS).
During the lockdown
State-wide curfew announced on March 18 has been followed by a nation-wide lockdown between March 25 and May 3. However, certain relaxations have been recommended by the state government from April 21 onwards. Some of the key measures undertaken during the lockdown period are:
Administrative Measures
Advisory groups and task forces were set up on – (i) COVID-19 prevention, (ii) Health and Economy, and (iii) Higher education. These groups will provide advice on the way forward for (i) prevention and containment activities, (ii) post-lockdown strategies and strategies to revive the economy, and (iii) to address the challenges facing the higher education sector respectively.
Services of retiring medical and paramedical professionals retiring between March and August have been extended till September 2020.
Essential Goods and Services
A Drug Supply Control Room was set up at the Rajasthan Pharmacy Council. This is to ensure uninterrupted supply of medicines during the lockdown and will also assist in facilitating home delivery of medicines.
The government permitted Fair Price Shops to sell products such as masalas, sanitisers, and hygiene products, in addition to food grains.
Village service cooperatives were declared as secondary markets to facilitate farmers to sell their produce near their own fields/villages during the lockdown.
A Whatsapp helpline was also set up for complaints regarding hoarding, black marketing, and overpricing.
Travel and Movement
Once lockdown was in place, the government issued instructions to identify, screen, and categorise people from other states who have travelled to Rajasthan. They were to be categorised into: (i) people displaying symptoms to be put in isolation wards, (ii) people over 60 years of age with symptoms and co-morbidities to be put in quarantine centres, and (iii) asymptomatic people to be home quarantined.
On March 28, the government announced the availability of buses to transport people during the lockdown. Further, stranded students in Kota were allowed to return to their respective states.
On April 2, a portal and a helpline were launched to help stranded foreign tourists and NRIs.
On April 11, an e-pass facility was launched for movement of people and vehicles.
Health Measures
To identify COVID-19 patients, district officials were instructed to monitor people with ARI/URI/Pneumonia or other breathing difficulties coming into hospital OPDs. Pharmacists were also instructed to not issue medicines for cold/cough without prescriptions.
A mobile app – Raj COVID Info – was developed by the government for tracking of quarantined people. Quarantined persons are required to send their selfie clicks at regular intervals, failing which a notification would be sent by the app. The app also provides a lot of information on COVID-19, such as the number of cases, and press releases by the government.
Due to the lockdown, people had restricted access to hospitals and treatment. Thus, instructions were issued to utilise Mobile Medical Vans for treatment/screening and also as mobile OPDs.
On April 20, a detailed action plan for prevention and control of COVID-19 was released. The report recommended: (i) preparation of a containment plan, (ii) formation of RRTs, (iii) testing protocols, (iv) setting up of control room and helpline, (v) designated quarantine centres and COVID-19 hospitals, (vi) roles and responsibilities, and (vii) other logistics.
Welfare Measures
The government issued instructions to make medicines available free of cost to senior citizens and other patients with chronic illnesses through the Chief Minister’s Free Medicine Scheme.
Rs 60 crore was allotted to Panchayati Raj Institutions to purchase PPEs and for other prevention activities.
A one-time cash transfer of Rs 1000 to over 15 lakh construction workers was announced. Similar cash transfer of Rs 1000 was announced for poor people who were deprived of livelihood during the lockdown, particularly those people with no social security benefits. Eligible families would be selected through the Aadhaar database. Further, an additional cash transfer of Rs 1500 to needy eligible families from different categories was announced.
The state also announced an aid of Rs 50 lakh to the families of frontline workers who lose their lives due to COVID-19.
To maintain social distancing, the government will conduct a door-to-door distribution of ration to select beneficiaries in rural areas of the state. The government also announced the distribution of free wheat for April, May, and June, under the National Food Security Act, 2013. Ration will also be distributed to stranded migrant families from Pakistan, living in the state.
The government announced free tractor & farming equipment on rent in tie-up with farming equipment manufacturers to assist economically weak small & marginal farmers.
Other Measures
Education: Project SMILE was launched to connect students and teachers online during the lockdown. Study material would be sent through specially formed Whatsapp groups. For each subject, 30-40 minute content videos have been prepared by the Education Department.
Industry: On April 18, new guidelines were issued for industries and enterprises to resume operations from April 20 onwards. Industries located in rural areas or export units / SEZs in municipal areas where accommodation facilities for workers are present, are allowed to function. Factories have been permitted to increase the working hours from 8 hours to 12 hours per day, to reduce the requirement of workers in factories. This exemption has been allowed for the next three months for factories operating at 60% to 65% of manpower capacity.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.