
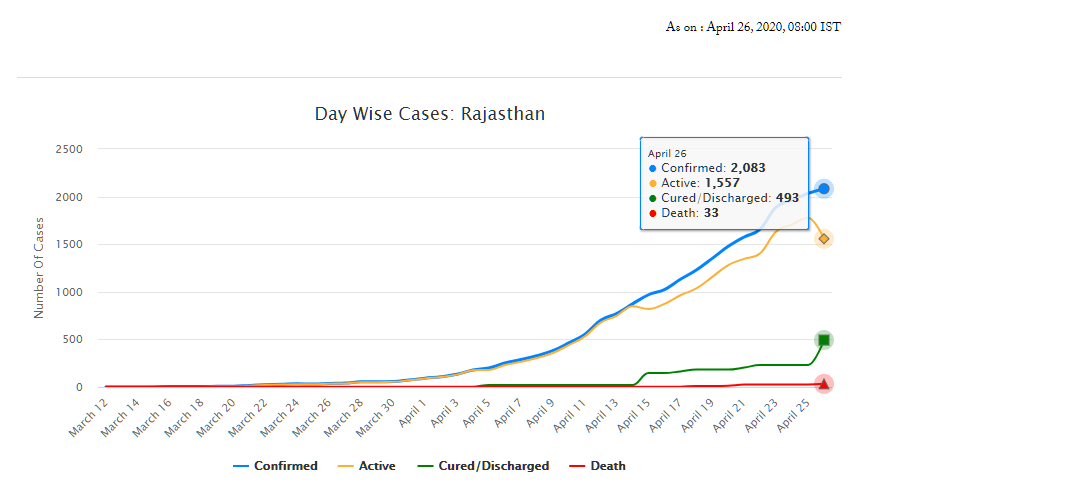
As of April 26, Rajasthan has 2,083 confirmed cases of COVID-19 (fifth highest in the country), of which 493 have recovered and 33 have died. On March 18, the Rajasthan government had declared a state-wide curfew till March 31, to check the spread of the disease. A nation-wide lockdown has also been in place since March 25 and is currently, extended up to May 3. The state has announced several policy decisions to prevent the spread of the virus and provide relief for those affected by it. This blog summarises the key policy measures taken by the Government of Rajasthan in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Early measures for containment
Between late January and early February, Rajasthan Government’s measures were aimed towards identification, screening and testing, and constant monitoring of passenger arrivals from China. Instructions were also issued to district health officials for various prevention, treatment, & control related activities, such as (i) mandatory 28-day home isolation for all travellers from China, (ii) running awareness campaigns, and (iii) ensuring adequate supplies of Personal Protection Equipments (PPEs). Some of the other measures, taken prior to the state-wide lockdown, are summarised below:
Administrative measures
The government announced the formation of Rapid Response Teams (RRTs), at the medical college-level and at district-level on March 3 and 5, respectively.
The District Collector was appointed as the Nodal Officer for all COVID-19 containment activities. Control Rooms were to be opened at all Sub-divisional offices. The concerned officers were also directed to strengthen information dissemination mechanisms and tackle the menace of fake news.
Directives were issued on March 11 to rural health workers/officials to report for duty on Gazetted holidays. Further, government departments were shut down between March 22 and March 31. Only essential departments such as Health Services were allowed to function on a rotation basis at 50% capacity and special / emergency leaves were permitted.
Travel and Movement
Air travellers were to undergo 14-day home isolation and were also required to provide an undertaking for the same. Besides, those violating the mandated isolation/quarantine were liable to be punished under Section. 188 of the Indian Penal Code. Penalties are imposed under this section on persons for the willful violation of orders that have been duly passed by a public servant.
All institutions and establishments, such as (i) educational institutions, theatres, and gyms, (ii) anganwadis, (iii) bars, discos, libraries, restaurants etc, (iv) museums and tourist places, were directed to be shut down till March 31.
The daily Jan Sunwai at the Chief Minister’s residence was cancelled until further notice. Various government offices were directed to shut down and exams of schools and colleges were postponed.
On March 24, the government issued a state-wide ban on the movement of private vehicles till March 31.
Health Measures
Advisories regarding prevention and control measures were issued to: (i) District Collectors, regarding sample collection and transportation, hotels, and preparedness of hospitals, (ii) Police department, to stop using breath analysers, (iii) Private hospitals, regarding preparedness and monitoring activities, and (iv) Temple trusts, to disinfect their premises with chemicals.
The government issued Standard Operating Procedures for conducting mock drills in emergency response handling of COVID-19 cases. Training and capacity building measures were also initiated for (i) Railways, Army personnel etc and (ii) ASHA workers, through video conferencing.
A model micro-plan for containing local transmission of COVID was released. Key features of the plan include: (i) identification and mapping of affected areas, (ii) activities for prevention control, surveillance, and contact tracing, (iii) human resource management, including roles and responsibilities, (iv) various infrastructural and logistical support, such as hospitals, labs etc, and (v) communication and data management.
Resource Management: Private hospitals and medical colleges were instructed to reserve 25 % of beds for COVID-19 patients. They were also instructed to utilise faculty from the departments of Preventive and Social Medicine to conduct health education and awareness activities.
Over 6000 Students of nursing schools were employed in assisting the health department to conduct screening activities being conducted at public places, railways stations, bus stands etc.
Further, the government issued guidelines to ensure the rational use of PPEs.
Welfare Measures
The government announced financial assistance, in the form of encouragement grants, to health professionals engaged in treating COVID-19 patients.
Steps were also taken by the government to ensure speedy disbursal of pensions for February and March.
The government also initiated the replacement of the biometric authentication with an OTP process for distribution of ration via the Public Distribution System (PDS).
During the lockdown
State-wide curfew announced on March 18 has been followed by a nation-wide lockdown between March 25 and May 3. However, certain relaxations have been recommended by the state government from April 21 onwards. Some of the key measures undertaken during the lockdown period are:
Administrative Measures
Advisory groups and task forces were set up on – (i) COVID-19 prevention, (ii) Health and Economy, and (iii) Higher education. These groups will provide advice on the way forward for (i) prevention and containment activities, (ii) post-lockdown strategies and strategies to revive the economy, and (iii) to address the challenges facing the higher education sector respectively.
Services of retiring medical and paramedical professionals retiring between March and August have been extended till September 2020.
Essential Goods and Services
A Drug Supply Control Room was set up at the Rajasthan Pharmacy Council. This is to ensure uninterrupted supply of medicines during the lockdown and will also assist in facilitating home delivery of medicines.
The government permitted Fair Price Shops to sell products such as masalas, sanitisers, and hygiene products, in addition to food grains.
Village service cooperatives were declared as secondary markets to facilitate farmers to sell their produce near their own fields/villages during the lockdown.
A Whatsapp helpline was also set up for complaints regarding hoarding, black marketing, and overpricing.
Travel and Movement
Once lockdown was in place, the government issued instructions to identify, screen, and categorise people from other states who have travelled to Rajasthan. They were to be categorised into: (i) people displaying symptoms to be put in isolation wards, (ii) people over 60 years of age with symptoms and co-morbidities to be put in quarantine centres, and (iii) asymptomatic people to be home quarantined.
On March 28, the government announced the availability of buses to transport people during the lockdown. Further, stranded students in Kota were allowed to return to their respective states.
On April 2, a portal and a helpline were launched to help stranded foreign tourists and NRIs.
On April 11, an e-pass facility was launched for movement of people and vehicles.
Health Measures
To identify COVID-19 patients, district officials were instructed to monitor people with ARI/URI/Pneumonia or other breathing difficulties coming into hospital OPDs. Pharmacists were also instructed to not issue medicines for cold/cough without prescriptions.
A mobile app – Raj COVID Info – was developed by the government for tracking of quarantined people. Quarantined persons are required to send their selfie clicks at regular intervals, failing which a notification would be sent by the app. The app also provides a lot of information on COVID-19, such as the number of cases, and press releases by the government.
Due to the lockdown, people had restricted access to hospitals and treatment. Thus, instructions were issued to utilise Mobile Medical Vans for treatment/screening and also as mobile OPDs.
On April 20, a detailed action plan for prevention and control of COVID-19 was released. The report recommended: (i) preparation of a containment plan, (ii) formation of RRTs, (iii) testing protocols, (iv) setting up of control room and helpline, (v) designated quarantine centres and COVID-19 hospitals, (vi) roles and responsibilities, and (vii) other logistics.
Welfare Measures
The government issued instructions to make medicines available free of cost to senior citizens and other patients with chronic illnesses through the Chief Minister’s Free Medicine Scheme.
Rs 60 crore was allotted to Panchayati Raj Institutions to purchase PPEs and for other prevention activities.
A one-time cash transfer of Rs 1000 to over 15 lakh construction workers was announced. Similar cash transfer of Rs 1000 was announced for poor people who were deprived of livelihood during the lockdown, particularly those people with no social security benefits. Eligible families would be selected through the Aadhaar database. Further, an additional cash transfer of Rs 1500 to needy eligible families from different categories was announced.
The state also announced an aid of Rs 50 lakh to the families of frontline workers who lose their lives due to COVID-19.
To maintain social distancing, the government will conduct a door-to-door distribution of ration to select beneficiaries in rural areas of the state. The government also announced the distribution of free wheat for April, May, and June, under the National Food Security Act, 2013. Ration will also be distributed to stranded migrant families from Pakistan, living in the state.
The government announced free tractor & farming equipment on rent in tie-up with farming equipment manufacturers to assist economically weak small & marginal farmers.
Other Measures
Education: Project SMILE was launched to connect students and teachers online during the lockdown. Study material would be sent through specially formed Whatsapp groups. For each subject, 30-40 minute content videos have been prepared by the Education Department.
Industry: On April 18, new guidelines were issued for industries and enterprises to resume operations from April 20 onwards. Industries located in rural areas or export units / SEZs in municipal areas where accommodation facilities for workers are present, are allowed to function. Factories have been permitted to increase the working hours from 8 hours to 12 hours per day, to reduce the requirement of workers in factories. This exemption has been allowed for the next three months for factories operating at 60% to 65% of manpower capacity.
For more information on the spread of COVID-19 and the central and state government response to the pandemic, please see here.
Today, the National Medical Commission Bill, 2019 was passed by Lok Sabha. It seeks to regulate medical education and practice in India. In 2017, a similar Bill had been introduced in Lok Sabha. It was examined by the Standing Committee on Health and Family Welfare, which recommended several changes to the Bill. However, the 2017 Bill lapsed with the dissolution of the 16th Lok Sabha. In this post, we analyse the 2019 Bill.
How is medical education and practice regulated currently?
The Medical Council of India (MCI) is responsible for regulating medical education and practice. Over the years, there have been several issues with the functioning of the MCI with respect to its regulatory role, composition, allegations of corruption, and lack of accountability. For example, MCI is an elected body where its members are elected by medical practitioners themselves, i.e., the regulator is elected by the regulated. Experts have recommended nomination based constitution of the MCI instead of election, and separating the regulation of medical education and medical practice. They suggested that legislative changes should be brought in to overhaul the functioning of the MCI.
To meet this objective, the Bill repeals the Indian Medical Council Act, 1956 and dissolves the current MCI.
The 2019 Bill sets up the National Medical Commission (NMC) as an umbrella regulatory body with certain other bodies under it. The NMC will subsume the MCI and will regulate medical education and practice in India. Under the Bill, states will establish their respective State Medical Councils within three years. These Councils will have a role similar to the NMC, at the state level.
Functions of the NMC include: (i) laying down policies for regulating medical institutions and medical professionals, (ii) assessing the requirements of human resources and infrastructure in healthcare, (iii) ensuring compliance by the State Medical Councils with the regulations made under the Bill, and (iv) framing guidelines for determination of fee for up to 50% of the seats in the private medical institutions.
Who will be a part of the NMC?
The Bill replaces the MCI with the NMC, whose members will be nominated. The NMC will consist of 25 members, including: (i) Director Generals of the Directorate General of Health Services and the Indian Council of Medical Research, (ii) Director of any of the AIIMS, (iii) five members (part-time) to be elected by the registered medical practitioners, and (iv) six members appointed on rotational basis from amongst the nominees of the states in the Medical Advisory Council.
Of these 25 members, at least 15 (60%) are medical practitioners. The MCI has been noted to be non-diverse and consists mostly of doctors who look out for their own self-interest over public interest. In order to reduce the monopoly of doctors, it has been recommended by experts that the MCI should include diverse stakeholders such as public health experts, social scientists, and health economists. For example, in the United Kingdom, the General Medical Council which is responsible for regulating medical education and practice consists of 12 medical practitioners and 12 lay members (such as community health members, administrators from local government).
What are the regulatory bodies being set up under the NMC?
The Bill sets up four autonomous boards under the supervision of the NMC. Each board will consist of a President and four members (of which two members will be part-time), appointed by the central government (on the recommendation of a search committee). These bodies are:
How is the Bill changing the eligibility guidelines for doctors to practice medicine?
There will be a uniform National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test for admission to under-graduate and post-graduate super-speciality medical education in all medical institutions regulated under the Bill. Further, the Bill introduces a common final year undergraduate examination called the National Exit Test for students graduating from medical institutions to obtain the license for practice. This test will also serve as the basis for admission into post-graduate courses at medical institutions under this Bill. Foreign medical practitioners may be permitted temporary registration to practice in India.
However, the Bill does not specify the validity period of this license to practice. In other countries such as the United Kingdom and Australia, a license to practice needs to be periodically renewed. For example, in the UK the license has to be renewed every five years, and in Australia it has to renewed annually.
How will the issues of medical misconduct be addressed?
The State Medical Council will receive complaints relating to professional or ethical misconduct against a registered medical practitioner. If the medical practitioner is aggrieved of a decision of the State Medical Council, he may appeal to the Ethics and Medical Registration Board. If the medical practitioner is aggrieved of the decision of the Board, he can approach the NMC to appeal against the decision. It is unclear why the NMC is an appellate authority with regard to matters related to professional or ethical misconduct of medical practitioners.
It may be argued that disputes related to ethics and misconduct in medical practice may require judicial expertise. For example, in the UK, the regulator for medical education and practice – the General Medical Council (GMC) receives complaints with regard to ethical misconduct and is required to do an initial documentary investigation in the matter and then forwards the complaint to a Tribunal. This Tribunal is a judicial body independent of the GMC. The adjudication decision and final disciplinary action is decided by the Tribunal.
How does the Bill regulate community health providers?
As of January 2018, the doctor to population ratio in India was 1:1655 compared to the World Health Organisation standard of 1:1000. To fill in the gaps of availability of medical professionals, the Bill provides for the NMC to grant limited license to certain mid-level practitioners called community health providers, connected with the modern medical profession to practice medicine. These mid-level medical practitioners may prescribe specified medicines in primary and preventive healthcare. However, in any other cases, these practitioners may only prescribe medicine under the supervision of a registered medical practitioner.
This is similar to other countries where medical professionals other than doctors are allowed to prescribe allopathic medicine. For example, Nurse Practitioners in the USA provide a full range of primary, acute, and specialty health care services, including ordering and performing diagnostic tests, and prescribing medications. For this purpose, Nurse Practitioners must complete a master's or doctoral degree program, advanced clinical training, and obtain a national certification.