
The central government has enforced a nation-wide lockdown between March 25 and May 3 as part of its measures to contain the spread of COVID-19. During the lockdown, several restrictions have been placed on the movement of individuals and economic activities have come to a halt barring the activities related to essential goods and services. The restrictions are being relaxed in less affected areas in a limited manner since April 20. In this blog, we look at how the lockdown has impacted the demand and supply of electricity and what possible repercussions its prolonged effect may have on the power sector.
Power supply saw a decrease of 25% during the lockdown (year-on-year)
As electricity cannot be stored in large amount, the power generation and supply for a given day are planned based on the forecast for demand. The months of January and February in 2020 had seen an increase of 3% and 7% in power supply, respectively as compared to 2019 (year-on-year). In comparison, the power supply saw a decrease of 3% between March 1 and March 24. During the lockdown between March 24 and April 19, the total power supply saw a decrease of about 25% (year-on-year).
Figure 1: % change in power supply position between March 1 and April 19 (Y-o-Y from 2019 to 2020)
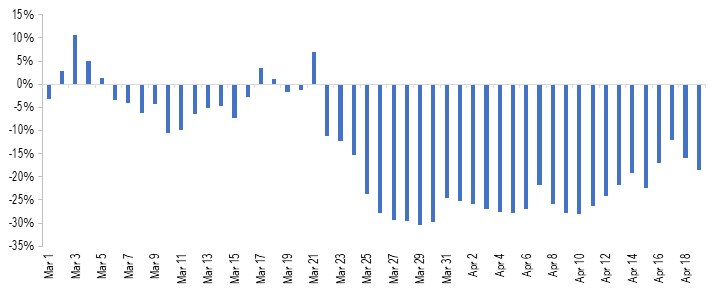
Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
If we look at the consumption pattern by consumer category, in 2018-19, 41% of total electricity consumption was for industrial purposes, followed by 25% for domestic and 18% for agricultural purposes. As the lockdown has severely reduced the industrial and commercial activities in the country, these segments would have seen a considerable decline in demand for electricity. However, note that the domestic demand may have seen an uptick as people are staying indoors.
Figure 2: Power consumption by consumer segment in 2018-19
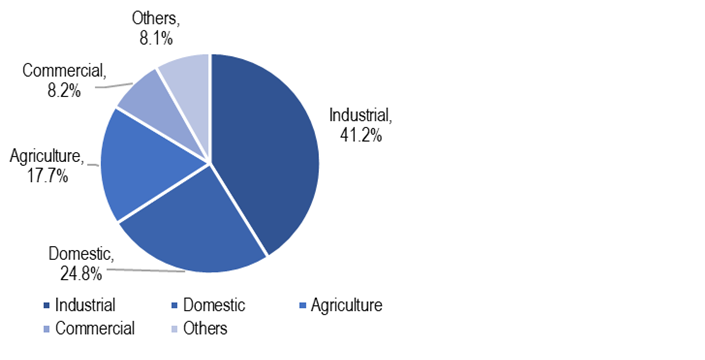
Sources: Central Electricity Authority; PRS.
Electricity demand may continue to be subdued over the next few months. At this point, it is unclear that when lockdown restrictions are eased, how soon will economic activities return to pre COVID-19 levels. India’s growth projections also highlight a slowdown in the economy in 2020 which will further impact the demand for electricity. On April 16, the International Monetary Fund has slashed its projection for India’s GDP growth in 2020 from 5.8% to 1.9%.
A nominal increase in energy and peak deficit levels
As power sector related operations have been classified as essential services, the plant operations and availability of fuel (primarily coal) have not been significantly constrained. This can be observed with the energy deficit and peak deficit levels during the lockdown period which have remained at a nominal level. Energy deficit indicates the shortfall in energy supply against the demand during the day. The average energy deficit between March 25 and April 19 has been 0.42% while the corresponding figure was 0.33% between March 1 and March 24. Similarly, the average peak deficit between March 25 and April 19 has been 0.56% as compared to 0.41% between March 1 and March 24. Peak deficit indicates the shortfall in supply against demand during highest consumption period in a day.
Figure 3: Energy deficit and peak deficit between March 1, 2020 and April 19, 2020 (in %)
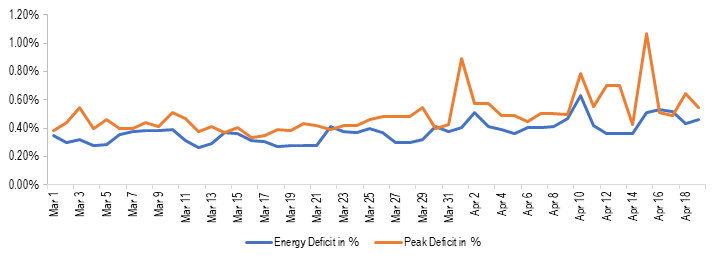
Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
Coal stock with power plants increases
Coal is the primary source of power generation in the country (~71% in March 2020). During the lockdown period, the coal stock with coal power plants has seen an increase. As of April 19, total coal-stock with the power plants in the country (in days) has risen to 29 days as compared to 24 days on March 24. This indicates that the supply of coal has not been constrained during the lockdown, at least to the extent of meeting the requirements of power plants.
Energy mix changes during the lockdown, power generation from coal impacted
During the lockdown, power generation has been adjusted to compensate for reduced consumption, Most of this reduction in consumption has been adjusted by reduced coal power generation. As can be seen in Table 1, coal power generation reduced from an average of 2,511 MU between March 1 and March 24 to 1,873 MU between March 25 and April 19 (about 25%). As a result, the contribution of coal in total power generation reduced from an average of 72.5% to 65.6% between these two periods.
Table 1: Energy Mix during March 1-April 19, 2020
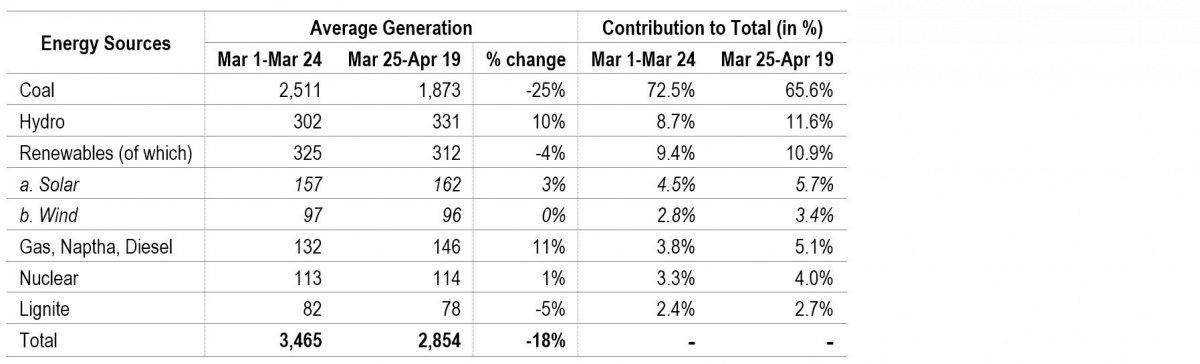
Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
This shift may be happening due to various reasons including: (i) renewable energy sources (solar, wind, and small hydro) have MUST RUN status, i.e., the power generated by them has to be given the highest priority by distribution companies, and (ii) running cost of renewable power plants is lower as compared to thermal power plants.
This suggests that if growth in electricity demand were to remain weak, the adverse impact on the coal power plants could be more as compared to other power generation sources. This will also translate into weak demand for coal in the country as almost 87% of the domestic coal production is used by the power sector. Note that the plant load factor (PLF) of the thermal power plants has seen a considerable decline over the years, decreasing from 77.5% in 2009-10 to 56.4% in 2019-20. Low PLF implies that coal plants have been lying idle. Coal power plants require significant fixed costs, and they incur such costs even when the plant is lying idle. The declining capacity utilisation augmented by a weaker demand will undermine the financial viability of these plants further.
Figure 4: Power generation from coal between March 1, 2020 and April 19, 2020 (in MU)
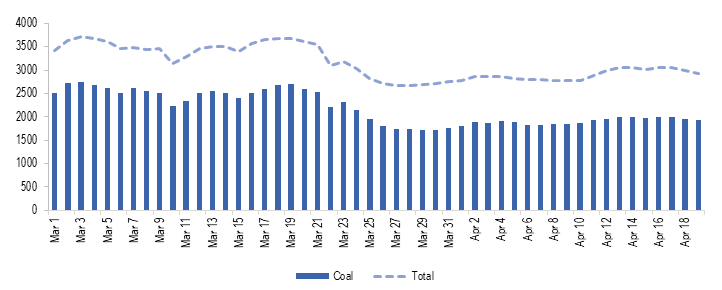
Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
Finances of the power sector to be severely impacted
Power distribution companies (discoms) buy power from generation companies and supply it to consumers. In India, most of the discoms are state-owned utilities. One of the key concerns in the Indian power sector has been the poor financial health of its discoms. The discoms have had high levels of debt and have been running losses. The debt problem was partly addressed under the UDAY scheme as state governments took over 75% of the debt of state-run discoms (around 2.1 lakh crore in two years 2015-16 and 2016-17). However, discoms have continued to register losses owing to underpricing of electricity tariff for some consumer segments, and other forms of technical and commercial losses. Outstanding dues of discoms towards power generation companies have also been increasing, indicating financial stress in some discoms. At the end of February 2020, the total outstanding dues of discoms to generation companies stood at Rs 92,602 crore.
Due to the lockdown and its further impact in the near term, the financial situation of discoms is likely to be aggravated. This will also impact other entities in the value chain including generation companies and their fuel suppliers. This may lead to reduced availability of working capital for these entities and an increase in the risk of NPAs in the sector. Note that, as of February 2020, the power sector has the largest share in the deployment of domestic bank credit among industries (Rs 5.4 lakh crore, 19.3% of total).
Following are some of the factors which have impacted the financial situation during the lockdown:
Reduced cross-subsidy: In most states, the electricity tariff for domestic and agriculture consumers is lower than the actual cost of supply. Along with the subsidy by the state governments, this gap in revenue is partly compensated by charging industrial and commercial consumers at a higher rate. Hence, industrial and commercial segments cross-subsidise the power consumption by domestic and agricultural consumers.
The lockdown has led to a halt on commercial and industrial activities while people are staying indoors. This has led to a situation where the demand from the consumer segments who cross-subsidise has decreased while the demand from consumer segments who are cross-subsidised has increased. Due to this, the gap between revenue realised by discoms and cost of supply will widen, leading to further losses for discoms. States may choose to bridge this gap by providing a higher subsidy.
Moratorium to consumers: To mitigate the financial hardship of citizens due to COVID-19, some states such as Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Goa, among others, have provided consumers with a moratorium for payment of electricity bills. At the same time, the discoms are required to continue supplying electricity. This will mean that the return for the supply made in March and April will be delayed, leading to lesser cash in hand for discoms.
Some state governments such as Bihar also announced a reduction in tariff for domestic and agricultural consumers. Although, the reduction in tariff will be compensated to discoms by government subsidy.
Constraints with government finances: The revenue collection of states has been severely impacted as economic activities have come to a halt. Further, the state governments are directing their resources for funding relief measures such as food distribution, direct cash transfers, and healthcare. This may adversely affect or delay the subsidy transfer to discoms.
The UDAY scheme also requires states to progressively fund greater share in losses of discoms from their budgetary resources (10% in 2018-19, 25% in 2019-20, and 50% in 2020-21). As losses of discoms may widen due to the above-mentioned factors, the state government’s financial burden is likely to increase.
Capacity addition may be adversely impacted
As per the National Electricity Plan, India’s total capacity addition target is around 176 GW for 2017-2022. This comprises of 118 GW from renewable sources, 6.8 GW from hydro sources, and 6.4 GW from coal (apart from 47.8 GW of coal-based power projects already in various stages of production as of January 2018).
India has set a goal of installing 175 GW of Renewable Power Capacity by 2022 as part of its climate change commitments (86 GW has been installed as of January 2020). In January 2020, the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Energy observed that India could only install 82% and 55% of its annual renewable energy capacity addition targets in 2017-18 and 2018-19. As of January 2020, 67% of the target has been achieved for 2019-20.
Due to the impact of COVID-19, the capacity addition targets for various sources is likely to be adversely impacted in the short run as:
construction activities were stopped during the lockdown and will take some time to return to normal,
disruption in the global supply chain may lead to difficulties with the availability of key components leading to delay in execution of projects, for instance, for solar power plants, solar PV modules are mainly imported from China, and
reduced revenue for companies due to weak demand will leave companies with less capacity left for capital expenditure.
Key reforms likely to be delayed
Following are some of the important reforms anticipated in 2020-21 which may get delayed due to the developing situation:
The real-time market for electricity: The real-time market for electricity was to be operationalised from April 1, 2020. However, the lockdown has led to delay in completion of testing and trial runs. The revised date for implementation is now June 1, 2020.
UDAY 2.0/ADITYA: A new scheme for the financial turnaround of discoms was likely to come this year. The scheme would have provided for the installation of smart meters and incentives for rationalisation of the tariff, among other things. It remains to be seen what this scheme would be like since the situation with government finances is also going to worsen due to anticipated economic slowdown.
Auction of coal blocks for commercial mining: The Coal Ministry has been considering auction of coal mines for commercial mining this year. 100% FDI has been allowed in the coal mining activity for commercial sale of coal to attract foreign players. However, the global economic slowdown may mean that the auctions may not generate enough interest from foreign as well as domestic players.
For a detailed analysis of the Indian Power Sector, please see here. For details on the number of daily COVID-19 cases in the country and across states, please see here. For details on the major COVID-19 related notifications released by the centre and the states, please see here.
The government's acquisition of land for projects has been facing protests across the country, the violence in Uttar Pradesh being only the latest. What is Land Acquisition? Land acquisition is the process by which the government forcibly acquires private property for public purpose without the consent of the land-owner. It is thus different from a land purchase, in which the sale is made by a willing seller. How is this process governed? Land Acquisition is governed by the Land Acquisition Act, 1894. The government has to follow a process of declaring the land to be acquired, notify the interested persons, and acquire the land after paying due compensation. Various state legislatures have also passed Acts that detail various aspects of the acquisition process. Land is a state subject. Why is Parliament passing a law? Though land is a state subject, "acquisition and requisitioning of property" is in the concurrent list. Both Parliament and state legislatures can make laws on this subject. Is there a new Act being proposed? The government had introduced a Bill to amend this Act in 2007. That Bill lapsed in 2009 at the time of the general elections. The government has stated its intent to re-introduce a similar Bill, but has not yet done so. What are the major changes being proposed? There are significant changes proposed in the 2007 Bill with regard to (a) the purpose for which land may be acquired; (b) the amount of compensation to be paid; (c) the process of acquisition; (d) use of the land acquired; and (e) dispute settlement mechanisms. We explain these briefly below. Purpose: Currently, land may be acquired for a range of uses such as village sites, town or rural planning, residential purposes for poor or displaced persons, planned development (education, housing, health, slum clearance), and for state corporations. Land may also be acquired for use by private companies for the above purposes or if the work "is likely to prove useful to the public". The 2007 Bill had a narrower list: (a) for strategic naval, military or air force purposes; (b) for public infrastructure projects; and (c) for any purpose useful to the general public if 70% of the land has been purchased from willing sellers through the free market. Compensation: The current Act requires market value to be paid for the land and any other property on it (buildings, trees, irrigation work etc) as well as expenses for compelling the person change place of residence or business. It explicitly prohibits taking into account the intended use of land while computing market value. The 2007 Bill requires payment of the highest of three items: the minimum value specified for stamp duty, the average of the top 50 per cent by price of land sale in the vicinity, and the average of the top 50 pc of the land purchased for the project from willing sellers. For computing recent land sale, the intended land use is to be used. Thus, agricultural land being acquired for an industrial project will be paid the price of industrial land. Process of acquisition: Several changes are proposed, including the requirement of a social impact assessment. Any project that displaces more than 400 families (200 in hilly, tribal and desert areas) will require an SIA before the acquisition is approved. Use of land acquired: The 2007 Bill requires the land acquired to be used for that purpose within five years. If this condition is not met, the land reverts to the government (it is not returned to the original land owners). If any acquired land is transferred to another entity, 80 pc of the capital gains has to be shared with the original land-owners and their legal heirs. Dispute Settlement: Currently, all disputes are resolved by civil courts, which results in delays. The 2007 Bill sets up Land Acquisition Compensation Dispute Resolution Authority at the state and national levels. These authorities will have the power of civil courts, and will adjudicate disputes related to compensation claims. Does the proposed Bill address the major issues? The Bill narrows the uses for which land may be acquired. It also changes the compensation due and links that to the market price for which land is to be used. There could be significant changes in acquisition for use by private industry. Firstly, they would have to purchase at least 70 pc of the required land from willing sellers (presumably, at fair market price). Second, the compensation amount for the remaining (upto 30 pc of land) could be significantly higher than the current method. This would be at a premium to the average paid to the willing sellers, and it would be based on intended industrial or commercial use which usually commands a higher price than agricultural land. However, the effect on acquisition for projects such as highways and railways will not be significant, as there is no benchmark for price determination for such use. This article appeared in Rediff News on May 12, 2011 and can be accessed here.