
Each year during the Budget Session, Rajya Sabha examines the working of certain ministries. This year it has identified four ministries for discussion, which includes the Ministry of Home Affairs. In light of this, we analyse some key functions of the Ministry and the challenges in carrying out these functions.
What are the key functions of Ministry of Home Affairs?
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is primarily responsible for: (i) maintenance of internal security, (ii) governance issues between the centre and states, and (iii) disaster management. It also discharges several other key functions that include: (i) border management, (ii) administration of union territories, (iii) implementation of provisions relating to the official languages, and (iv) conducting the population census every ten years.
Under the Constitution, ‘public order’ and ‘police’ are state list subjects. The MHA assists the state governments by providing them: (i) central armed police forces, and (ii) financial assistance for modernising state police forces, communication equipment, weaponry, mobility, training and other police infrastructure.
What is the role of the central armed police forces?
 The MHA manages seven central police forces: (i) Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) which assists in internal security and law and order, (ii) Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) which protects vital installations (like airports) and public sector undertakings, (iii) National Security Guards which is a special counter-terrorism force, and (iv) four border guarding forces, namely, Border Security Force (BSF), Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP), Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) and Assam Rifles (AR).
The MHA manages seven central police forces: (i) Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) which assists in internal security and law and order, (ii) Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) which protects vital installations (like airports) and public sector undertakings, (iii) National Security Guards which is a special counter-terrorism force, and (iv) four border guarding forces, namely, Border Security Force (BSF), Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP), Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) and Assam Rifles (AR).
As of January 2017, the total sanctioned strength of the seven CAPFs was 10. 8 lakhs. However, 15% of these posts (i.e., about 1.6 lakhs posts) were lying vacant. The vacancy in the CAPFs has remained above 7% for the last five years (see Table 1). In 2017, the Sashastra Seema Bal had the highest vacancy (57%). The CRPF, which accounts for 30% of the total sanctioned strength of the seven CAPFs, had a vacancy of 8%.
How does MHA assist the police forces?
In Union Budget 2018-19, Rs 1,07,573 crore has been allocated to the Ministry of Home Affairs. The Ministry has estimated to spend 82% of this amount on police. The remaining allocation is towards grants to Union Territories, and other items including disaster management, rehabilitation of refugees and migrants, and the Union Cabinet.
The MHA has been implementing Modernisation of Police Forces (MPF) scheme since 1969 to supplement the resources of states for modernising their police forces. Funds from the MPF scheme are utilised for improving police infrastructure through construction of police stations, and provision of modern weaponry, surveillance, and communication equipment. Some other important objectives under the scheme include upgradation of training infrastructure, police housing, and computerisation.
The scheme has undergone revision over the years. A total allocation of Rs 11,946 crore was approved for the MPF scheme, for a five-year period between 2012-13 to 2016-17. Following the recommendations of the 14th Finance Commission (to increase the share of central taxes to states), it was decided that the MPF scheme would be delinked from central government funding from 2015-16 onwards. However, in September 2017, the Union Cabinet approved an outlay of Rs 25,060 crore under the scheme, for the period 2017-18 to 2019-20. The central government will provide about 75% of this amount, and the states will provide the remaining 25%.
The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) has found that weaponry in several state police forces is outdated, and there is a shortage of arms and ammunitions. An audit of Rajasthan police force(2009-14) found that there was a shortage of 75% in the availability of modern weapons against the state’s requirements. In case of West Bengal and Gujarat police forces, CAG found a shortage of 71% and 36% respectively. Further, there has been a persistent problem of underutilisation of modernisation funds by the states. Figure 1 shows the level of utilisation of modernisation funds by states between 2010-11 and 2016-17.

What are the major internal security challenges in India?
Maintaining internal security of the country is one of the key functions of the MHA. The major internal security challenges that India faces are: (i) terrorist activities in the country, (ii) cross-border terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir, (iii) Left Wing Extremism in certain areas, and (iv) insurgency in the North-Eastern states.
Between 2015 and 2016, the number of cross-border infiltrations in Jammu and Kashmir increased by almost three times, from 121 to 364. On the other hand, incidents of insurgency in Left Wing Extremism areas have decreased from 1,048 in 2016 to 908 in 2017.
The Standing Committee on Home Affairs noted in 2017-18 that security forces in Jammu and Kashmir are occupied with law and order incidents, such as stone pelting, which gives militants the time to reorganise and perpetrate terror attacks. The Committee recommended that the MHA should adopt a multi-pronged strategy that prevents youth from joining militancy, curbs their financing, and simultaneously launch counter-insurgency operations.
In relation to Left Wing Extremism, the Standing Committee (2017) observed that police and paramilitary personnel were getting killed because of mine blasts and ambushes. It recommended that the MHA should make efforts to procure mine-resistant vehicles. This could be done through import or domestic manufacturing under the ‘Make in India’ programme.
What is the MHA’s role in border management?
India has a land border of over 15,000 kms, which it shares with seven countries (Pakistan, China, Bangladesh, Nepal, Myanmar, Bhutan, and Afghanistan). Further, it has a coastline of over 7,500 kms. The MHA is responsible for: (i) management of international lands and coastal borders, (ii) strengthening of border guarding, and (iii) creation of infrastructure such as roads, fencing, and lighting of borders.
Construction of border outposts is one of the components of infrastructure at border areas. The Standing Committee on Home Affairs (2017) noted that the proposal to construct 509 outposts along the India-Bangladesh, and India-Pakistan borders had been reduced to 422 outposts in 2016. It recommended that such a reduction should be reconsidered since 509 outposts would reduce the inter-border outpost distance to 3.5 kms, which is important for the security of the country.
How is coastal security carried out?
Coastal security is jointly carried out by the Indian Navy, Indian Coast Guard, and marine police of coastal states and Union Territories. The MHA is implementing the Coastal Security Scheme to strengthen the marine police of nine coastal states and four Union Territories by enhancing surveillance, and improve patrolling in coastal areas. Under this scheme, the Ministry sought to construct coastal police stations, purchase boats, and acquire vehicles for patrolling on land, among other objectives.
The Standing Committee on Home Affairs (2017) observed that the implementation of Phase-II of this scheme within the set time-frame has not been possible. It also noted that there was lack of coordination between the Indian Navy, the Indian Coast Guard, and the coastal police. In this context, the Committee recommended that the Director General, Indian Coast Guard, should be the nodal authority for coordinating operations related to coastal security.
The central government has enforced a nation-wide lockdown between March 25 and May 3 as part of its measures to contain the spread of COVID-19. During the lockdown, several restrictions have been placed on the movement of individuals and economic activities have come to a halt barring the activities related to essential goods and services. The restrictions are being relaxed in less affected areas in a limited manner since April 20. In this blog, we look at how the lockdown has impacted the demand and supply of electricity and what possible repercussions its prolonged effect may have on the power sector.
Power supply saw a decrease of 25% during the lockdown (year-on-year)
As electricity cannot be stored in large amount, the power generation and supply for a given day are planned based on the forecast for demand. The months of January and February in 2020 had seen an increase of 3% and 7% in power supply, respectively as compared to 2019 (year-on-year). In comparison, the power supply saw a decrease of 3% between March 1 and March 24. During the lockdown between March 24 and April 19, the total power supply saw a decrease of about 25% (year-on-year).
Figure 1: % change in power supply position between March 1 and April 19 (Y-o-Y from 2019 to 2020)
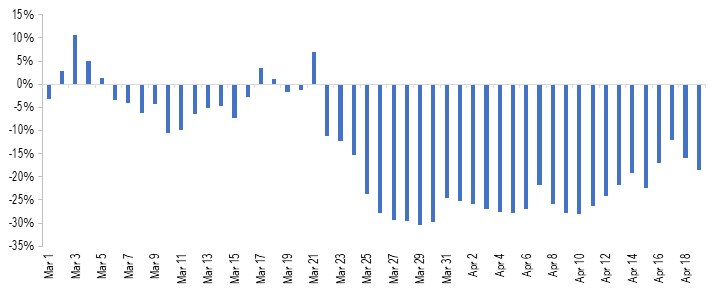
Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
If we look at the consumption pattern by consumer category, in 2018-19, 41% of total electricity consumption was for industrial purposes, followed by 25% for domestic and 18% for agricultural purposes. As the lockdown has severely reduced the industrial and commercial activities in the country, these segments would have seen a considerable decline in demand for electricity. However, note that the domestic demand may have seen an uptick as people are staying indoors.
Figure 2: Power consumption by consumer segment in 2018-19
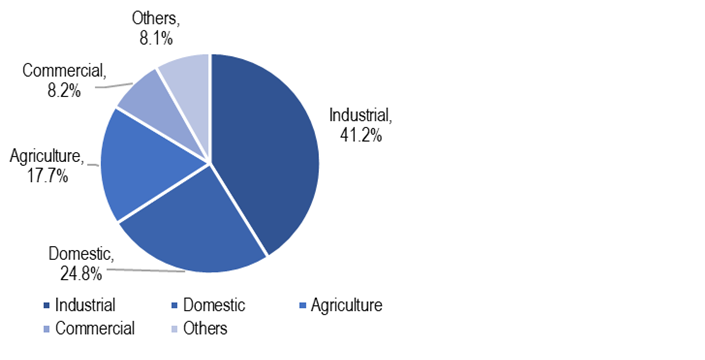
Sources: Central Electricity Authority; PRS.
Electricity demand may continue to be subdued over the next few months. At this point, it is unclear that when lockdown restrictions are eased, how soon will economic activities return to pre COVID-19 levels. India’s growth projections also highlight a slowdown in the economy in 2020 which will further impact the demand for electricity. On April 16, the International Monetary Fund has slashed its projection for India’s GDP growth in 2020 from 5.8% to 1.9%.
A nominal increase in energy and peak deficit levels
As power sector related operations have been classified as essential services, the plant operations and availability of fuel (primarily coal) have not been significantly constrained. This can be observed with the energy deficit and peak deficit levels during the lockdown period which have remained at a nominal level. Energy deficit indicates the shortfall in energy supply against the demand during the day. The average energy deficit between March 25 and April 19 has been 0.42% while the corresponding figure was 0.33% between March 1 and March 24. Similarly, the average peak deficit between March 25 and April 19 has been 0.56% as compared to 0.41% between March 1 and March 24. Peak deficit indicates the shortfall in supply against demand during highest consumption period in a day.
Figure 3: Energy deficit and peak deficit between March 1, 2020 and April 19, 2020 (in %)
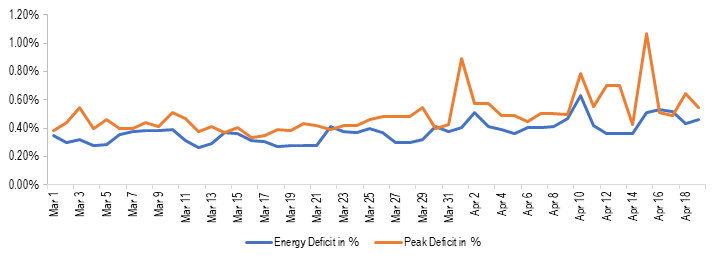
Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
Coal stock with power plants increases
Coal is the primary source of power generation in the country (~71% in March 2020). During the lockdown period, the coal stock with coal power plants has seen an increase. As of April 19, total coal-stock with the power plants in the country (in days) has risen to 29 days as compared to 24 days on March 24. This indicates that the supply of coal has not been constrained during the lockdown, at least to the extent of meeting the requirements of power plants.
Energy mix changes during the lockdown, power generation from coal impacted
During the lockdown, power generation has been adjusted to compensate for reduced consumption, Most of this reduction in consumption has been adjusted by reduced coal power generation. As can be seen in Table 1, coal power generation reduced from an average of 2,511 MU between March 1 and March 24 to 1,873 MU between March 25 and April 19 (about 25%). As a result, the contribution of coal in total power generation reduced from an average of 72.5% to 65.6% between these two periods.
Table 1: Energy Mix during March 1-April 19, 2020
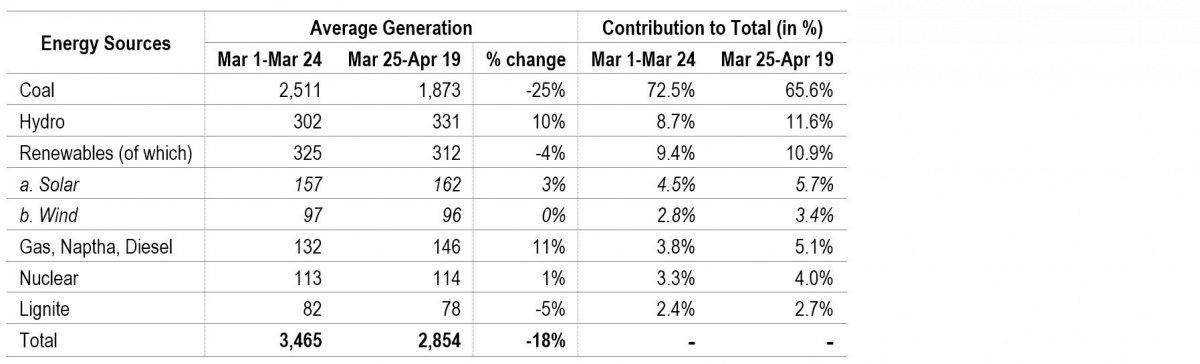
Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
This shift may be happening due to various reasons including: (i) renewable energy sources (solar, wind, and small hydro) have MUST RUN status, i.e., the power generated by them has to be given the highest priority by distribution companies, and (ii) running cost of renewable power plants is lower as compared to thermal power plants.
This suggests that if growth in electricity demand were to remain weak, the adverse impact on the coal power plants could be more as compared to other power generation sources. This will also translate into weak demand for coal in the country as almost 87% of the domestic coal production is used by the power sector. Note that the plant load factor (PLF) of the thermal power plants has seen a considerable decline over the years, decreasing from 77.5% in 2009-10 to 56.4% in 2019-20. Low PLF implies that coal plants have been lying idle. Coal power plants require significant fixed costs, and they incur such costs even when the plant is lying idle. The declining capacity utilisation augmented by a weaker demand will undermine the financial viability of these plants further.
Figure 4: Power generation from coal between March 1, 2020 and April 19, 2020 (in MU)
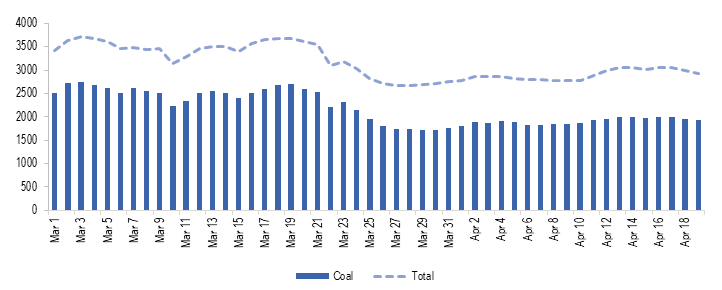
Sources: Daily Reports; POSOCO; PRS.
Finances of the power sector to be severely impacted
Power distribution companies (discoms) buy power from generation companies and supply it to consumers. In India, most of the discoms are state-owned utilities. One of the key concerns in the Indian power sector has been the poor financial health of its discoms. The discoms have had high levels of debt and have been running losses. The debt problem was partly addressed under the UDAY scheme as state governments took over 75% of the debt of state-run discoms (around 2.1 lakh crore in two years 2015-16 and 2016-17). However, discoms have continued to register losses owing to underpricing of electricity tariff for some consumer segments, and other forms of technical and commercial losses. Outstanding dues of discoms towards power generation companies have also been increasing, indicating financial stress in some discoms. At the end of February 2020, the total outstanding dues of discoms to generation companies stood at Rs 92,602 crore.
Due to the lockdown and its further impact in the near term, the financial situation of discoms is likely to be aggravated. This will also impact other entities in the value chain including generation companies and their fuel suppliers. This may lead to reduced availability of working capital for these entities and an increase in the risk of NPAs in the sector. Note that, as of February 2020, the power sector has the largest share in the deployment of domestic bank credit among industries (Rs 5.4 lakh crore, 19.3% of total).
Following are some of the factors which have impacted the financial situation during the lockdown:
Reduced cross-subsidy: In most states, the electricity tariff for domestic and agriculture consumers is lower than the actual cost of supply. Along with the subsidy by the state governments, this gap in revenue is partly compensated by charging industrial and commercial consumers at a higher rate. Hence, industrial and commercial segments cross-subsidise the power consumption by domestic and agricultural consumers.
The lockdown has led to a halt on commercial and industrial activities while people are staying indoors. This has led to a situation where the demand from the consumer segments who cross-subsidise has decreased while the demand from consumer segments who are cross-subsidised has increased. Due to this, the gap between revenue realised by discoms and cost of supply will widen, leading to further losses for discoms. States may choose to bridge this gap by providing a higher subsidy.
Moratorium to consumers: To mitigate the financial hardship of citizens due to COVID-19, some states such as Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Goa, among others, have provided consumers with a moratorium for payment of electricity bills. At the same time, the discoms are required to continue supplying electricity. This will mean that the return for the supply made in March and April will be delayed, leading to lesser cash in hand for discoms.
Some state governments such as Bihar also announced a reduction in tariff for domestic and agricultural consumers. Although, the reduction in tariff will be compensated to discoms by government subsidy.
Constraints with government finances: The revenue collection of states has been severely impacted as economic activities have come to a halt. Further, the state governments are directing their resources for funding relief measures such as food distribution, direct cash transfers, and healthcare. This may adversely affect or delay the subsidy transfer to discoms.
The UDAY scheme also requires states to progressively fund greater share in losses of discoms from their budgetary resources (10% in 2018-19, 25% in 2019-20, and 50% in 2020-21). As losses of discoms may widen due to the above-mentioned factors, the state government’s financial burden is likely to increase.
Capacity addition may be adversely impacted
As per the National Electricity Plan, India’s total capacity addition target is around 176 GW for 2017-2022. This comprises of 118 GW from renewable sources, 6.8 GW from hydro sources, and 6.4 GW from coal (apart from 47.8 GW of coal-based power projects already in various stages of production as of January 2018).
India has set a goal of installing 175 GW of Renewable Power Capacity by 2022 as part of its climate change commitments (86 GW has been installed as of January 2020). In January 2020, the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Energy observed that India could only install 82% and 55% of its annual renewable energy capacity addition targets in 2017-18 and 2018-19. As of January 2020, 67% of the target has been achieved for 2019-20.
Due to the impact of COVID-19, the capacity addition targets for various sources is likely to be adversely impacted in the short run as:
construction activities were stopped during the lockdown and will take some time to return to normal,
disruption in the global supply chain may lead to difficulties with the availability of key components leading to delay in execution of projects, for instance, for solar power plants, solar PV modules are mainly imported from China, and
reduced revenue for companies due to weak demand will leave companies with less capacity left for capital expenditure.
Key reforms likely to be delayed
Following are some of the important reforms anticipated in 2020-21 which may get delayed due to the developing situation:
The real-time market for electricity: The real-time market for electricity was to be operationalised from April 1, 2020. However, the lockdown has led to delay in completion of testing and trial runs. The revised date for implementation is now June 1, 2020.
UDAY 2.0/ADITYA: A new scheme for the financial turnaround of discoms was likely to come this year. The scheme would have provided for the installation of smart meters and incentives for rationalisation of the tariff, among other things. It remains to be seen what this scheme would be like since the situation with government finances is also going to worsen due to anticipated economic slowdown.
Auction of coal blocks for commercial mining: The Coal Ministry has been considering auction of coal mines for commercial mining this year. 100% FDI has been allowed in the coal mining activity for commercial sale of coal to attract foreign players. However, the global economic slowdown may mean that the auctions may not generate enough interest from foreign as well as domestic players.
For a detailed analysis of the Indian Power Sector, please see here. For details on the number of daily COVID-19 cases in the country and across states, please see here. For details on the major COVID-19 related notifications released by the centre and the states, please see here.